ActiveNature Season 13. Sun of a Beach

ActiveNature Season 13. Sun of a Beach
2025
Interesting and rare moments of everyday life on the best beaches.
Nature
Season 12. Past Bonus
Season 13. Past Bonus
Bali Beach, Maldives Beach, Mauritius Beach, Zanzibar Beach
Season 14. Future Bonus
Season 15. Future Bonus
Season 17. Future Bonus
Season 18. Future Bonus
| Activity | Hobby |
| Shark swimming | F1 Simulator |
| Iguana swimming | Karting |
| Turtle swimming | Football |
| Dolphin swimming | Volleyball |
| Sea lion swimming | Darts |
| Sandboarding | Chess |
| Drift taxi | Golf |
| Maglev | Skateboard |
| Ferris wheel | Drawing |
| Buggy | Dancing |
_
Season 1. Bonus.
City Insight
Belarus: Zembin
_
Place Insight
Resorts: Hampton by Hilton Minsk City Centre
_
Season 3. Bonus.
City Insight
Turkey: Arnavutkoy
_
Season 4. Past Bonus.
Place Insight
Wildlife: Maldives Beach
Season 5. Bonus.
City Insight
Cuba: Havana, Matanzas, Varadero
_
Place Insight
Resorts: Gran Hotel Bristol by Kempinski Havana
Wildlife: Varadero Beach
_
Season 6. Bonus.
City Insight
Argentina: Puerto Iguazu
Brazil: Foz do Iguacu, Indaiatuba, Manaus
Ecuador: Guayaquil, Puerto Ayora, Puerto Baquerizo Moreno, Puerto Villamil
Panama: Panama City
_
Place Insight
Heritage: Easter Island, Nazca lines, Palpa Lines, Panama Canal
National Parks: Rapa Nui
Resorts: Courtyard by Marriott Santiago
Wildlife: Amazon, Andes, Galapagos, Iguazu
_
Season 7. Bonus.
City Insight
Ethiopia: Addis Ababa
_
Place Insight. Past Bonus
Wildlife: Mauritius Beach, Zanzibar Beach
_
Season 8. Past Bonus.
Place Insight
Wildlife: Bali Beach
_
Stats: Countries 5 (93), Cities 20 (460), Events 0 (65), Places (HandMade+Nature) 17 (118), Activity 10 (30), Hobby 10 (30)
AI Procurement. Comparison of Traditional vs. Philosophy-Inspired Supply Chain Approaches
AI Procurement
Comparison of Traditional vs. Philosophy-Inspired Supply Chain Approaches
10.01.2025
Traditional Approach
Core Philosophy: Maximize efficiency, minimize cost, optimize shareholder value
Key Characteristics:
- Transactional supplier relationships
- Cost-driven decision making
- Just-in-time inventory (minimal buffers)
- Standardized, scalable processes
- Hierarchical control structures
- Risk transfer to suppliers
- Key metrics: Cost savings, ROI, on-time delivery
Pros:
- Predictable, measurable outcomes
- Scalable across global operations
- Proven frameworks and technologies
- Clear accountability structures
- Efficient in stable environments
Cons:
- Fragile during disruptions
- Human elements often overlooked
- Sustainability as add-on, not core
- Innovation stifled by standardization
- High burnout rates in operations
Philosophy-Inspired Approaches Comparison
| Philosophy | Core Focus | Procurement/SCM Application | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ikigai | Purpose-driven balance | Align processes with meaning, mission, profit | – Holistic value creation – Strong employee engagement – Balanced metrics |
– Can dilute financial focus – Complex to measure “purpose” |
| Lagom | “Just the right amount” | Balanced inventory, fair relationships, sustainable sourcing | – Resilient buffers – Sustainable by design – Reduces waste |
– May appear “unambitious” – Hard to quantify “enough” |
| Hygge | Comfort & human connection | Trust-based partnerships, pleasant work environments | – Strong supplier loyalty – Low team turnover – Collaborative innovation |
– May slow tough decisions – Could enable complacency |
| Sisū | Grit & resilience | Extreme preparedness, crisis-hardened networks | – Unbreakable during disruptions – Innovative under pressure – Strong crisis leadership |
– Risk of burnout – Can over-invest in redundancy |
| Ubuntu | Interconnected humanity | Community-centric sourcing, stakeholder inclusion | – Deep social license to operate – Unparalleled local resilience – Ethical brand strength |
– Highest cost structure – Complex stakeholder management |
| Wabi-Sabi | Embracing imperfection | Flexible systems, natural variation acceptance | – Adapts beautifully to flux – Reduces perfectionism waste – Authentic sustainability |
– Challenges quality standards – Difficult to scale uniformly |
| Jugaad | Frugal innovation | Resource-constrained problem solving | – Extreme cost efficiency – Hyper-local adaptability – Rapid crisis response |
– Quality control challenges – Difficult to systematize |
Effectiveness Analysis
Which is “More Effective”?
The answer depends entirely on the company’s context:
1. For Multinationals in Stable Markets:
- Primary: Traditional + Lagom hybrid
- Why: Maintains efficiency while adding resilience buffers and sustainability
- Effectiveness: High for predictable ROI with reduced disruption risk
2. For Socially-Conscious Brands:
- Primary: Ubuntu + Ikigai fusion
- Why: Authentic alignment with ethical consumer expectations
- Effectiveness: Creates powerful brand differentiation and loyalty
3. For Operations in Volatile Regions:
- Primary: Jugaad + Sisū combination
- Why: Maximizes survival and adaptation in constrained environments
- Effectiveness: Exceptional for maintaining operations against odds
4. For Luxury/Artisanal Businesses:
- Primary: Wabi-Sabi + Hygge blend
- Why: Values craftsmanship, story, and human relationships
- Effectiveness: Creates premium perceived value and customer connection
5. For Post-Crisis Recovery:
- Primary: Sisū + Jugaad with Ikigai
- Why: Combines resilience, resourcefulness, and renewed purpose
- Effectiveness: Rapid rebuilding with stronger foundations
Integrated Framework: The “Adaptive Purpose” Supply Chain
Most effective approach for the 21st century company:
Core Architecture:
1. Purpose Foundation (Ikigai) – Why do we exist beyond profit?
2. Balanced Operations (Lagom) – “Just right” inventory, partnerships, growth
3. Human Core (Hygge/Ubuntu) – Trust, dignity, and well-being at center
4. Resilience Layer (Sisū) – Grit and preparedness for disruptions
5. Adaptive Mindset (Wabi-Sabi/Jugaad) – Flexibility and frugal innovation
Implementation Strategy:
Stage 1: Traditional efficiency (financial viability)
Stage 2: + Lagom balance + Hygge relationships (stability)
Stage 3: + Ubuntu ethics + Ikigai purpose (meaning)
Stage 4: + Sisū resilience + Wabi-Sabi flexibility (adaptation)
Stage 5: + Jugaad innovation (thriving in constraints)
Pros of This Blended Approach:
- Addresses financial, social, environmental, and operational needs
- Creates both efficiency and resilience
- Attracts talent and builds brand across stakeholder groups
- Functions well in both stable and volatile conditions
- Continuously evolves through learning
Cons:
- Extremely complex to implement and measure
- Requires exceptional leadership and cultural maturity
- May face investor skepticism about “soft” metrics
- Integration challenges between conflicting priorities
Conclusion: The Evolution of Effectiveness
Traditional approaches are no longer sufficient in a world of climate disruption, pandemics, social inequality, and geopolitical volatility. However, pure philosophy-based approaches often lack the financial discipline required for survival.
The most effective modern supply chain is a hybrid: It begins with traditional financial discipline but layers on purpose (Ikigai), balance (Lagom), humanity (Ubuntu/Hygge), resilience (Sisū), and adaptive creativity (Wabi-Sabi/Jugaad) in proportions appropriate to the business context.
Effectiveness Metric Shift:
- Past: Cost savings + On-time delivery
- Present: Resilience + Sustainability + Profit
- Future: Regenerative impact + Stakeholder well-being + Adaptive innovation + Financial health
The company that masters contextual integration of these philosophies—knowing when to apply which principles—will build not just a supply chain, but a living business ecosystem that thrives through whatever challenges the 21st century presents. This requires moving from “either/or” thinking to “both/and” thinking—where a supply chain can be both efficient AND humane, both profitable AND purposeful, both standardized AND adaptable.
Final verdict: No single philosophy is “most effective.” The future belongs to philosophically intelligent organizations that can dynamically apply the right principles to the right situations, creating supply chains that are as wise as they are efficient.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Jugaad philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Jugaad philosophy?
09.01.2025
Integrating the Indian philosophy of Jugaad (pronounced joo-gaardh) — meaning “frugal innovation” or “the art of improvising effective solutions with limited resources” — into procurement and supply chain processes can create a culture of agility, resilience, and grassroots ingenuity.
Unlike top-down, capital-intensive optimization models, Jugaad is about flexibility, simplicity, and making things work in constrained, unpredictable environments.
Core Principles of Jugaad in Business
1. Do More with Less – Maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste.
2. Embrace Simplicity – Seek elegant, minimal, and accessible solutions over complex ones.
3. Think and Act Flexibly – Be agile and adapt quickly to changing constraints.
4. Include the Marginal – Innovate for and with underserved or constrained contexts.
5. Follow Your Heart – Passion and intuitive problem-solving drive action.
6. Learn Through Trial & Error – Experiment rapidly and learn from failure.
Practical Application to Procurement & Supply Chain
1. Supplier Strategy: Leveraging Grassroots & Frugal Partners
- Source from “Jugaad Entrepreneurs” – Actively seek out small, local, or informal sector suppliers who excel at frugal innovation. They often create robust, low-cost solutions perfect for emerging markets or resilient backup sourcing.
- Co-Innovate with Suppliers on Constraints – Challenge suppliers with clear constraints (e.g., “Reduce packaging cost by 30% without compromising protection”) and reward innovative, simple solutions.
- Develop Local “Micro-Supply Hubs” – Instead of relying solely on large centralized suppliers, create networks of local small suppliers who can respond quickly with flexible capacity.
2. Inventory & Logistics: Frugal & Adaptive Systems
- Create “Good Enough” Buffer Solutions – Use low-cost, locally available materials for packaging or in-house storage solutions (e.g., repurposed containers, modular DIY racks) instead of expensive custom systems.
- Flexible, Multi-Use Assets – Invest in logistics assets that can serve multiple purposes (e.g., vehicles that can handle different load types, modular containers).
- Last-Mile Jugaad – In challenging delivery environments (e.g., rural areas, dense urban markets), partner with local informal logistics networks (bicycle couriers, tuk-tuks, boat networks) who can navigate constraints creatively.
3. Process Design: Simplification & Improvisation
- “Minimum Viable Process” Approach – For non-critical procurement categories, design extremely simple, low-admin processes (e.g., delegated spot buying with basic guidelines) instead of over-engineered systems.
- Empower Frontline Improvisation – Train and trust procurement & logistics staff to solve problems on the ground with available resources (within ethical/legal boundaries). Celebrate stories of clever fixes.
- Low-Tech Digital Solutions – In areas with poor IT infrastructure, use lightweight tools like WhatsApp groups for supplier coordination, SMS-based tracking, or simple mobile apps instead of expensive, complex ERP extensions.
4. Risk Management & Resilience: Frugal Redundancy
- Build a “Jugaad Network” of Backup Options – Identify alternative materials, components, or routes that are less ideal but “good enough” in a crisis. Often these are local, slower, or non-standard but reliable under disruption.
- Cross-Train for Flexibility – Ensure team members can handle multiple roles (sourcing, logistics, basic quality checks) to maintain operations during shortages or absences.
- Design for Repair & Reuse – Procure equipment and assets that are easy to fix locally with generic parts, reducing downtime and dependence on expensive specialized service contracts.
5. Sustainability & Cost Innovation
- Waste-to-Value Initiatives – Apply Jugaad thinking to turn supply chain waste into resources (e.g., using pallet wood for in-house repairs, converting damaged goods into by-products).
- Frugal Automation – Instead of large-scale robotics, implement simple, low-cost automation (e.g., gravity-fed racks, manual conveyor improvements) that enhances productivity without major capex.
- Constraint-Driven Green Solutions – Use resource constraints (e.g., water scarcity, high energy costs) as drivers for innovative, low-cost sustainable practices.
Example: A Consumer Goods Company in Emerging Markets Applying Jugaad
- Procurement: Sources packaging from local small producers who make boxes from recycled agricultural waste, cutting costs and carbon.
- Production: Uses flexible, multi-skilled local labor to run small batch production lines that can quickly switch between products based on material availability.
- Distribution: For rural distribution, uses a hybrid model — trucks to regional hubs, then a network of motorized rickshaws with custom racks for last-mile delivery.
- Maintenance: Trains local technicians to repair factory equipment using 3D-printed parts and locally sourced components, avoiding expensive imported spare parts.
- Crisis Response: During a sudden border closure, the logistics team quickly partners with a local boat operator to move critical shipments via river routes at 1/10th the cost of air freight.
Contrast with Traditional Models
- Traditional: “Perfect solution” – Requires extensive planning, capital, and ideal conditions.
- Jugaad-Inspired: “Workable solution” – Focuses on speed, adaptability, and making the most of what’s available now.
Strategic Advantages of a Jugaad Supply Chain
1. Extreme Cost Efficiency – Reduces both capex and opex through frugal innovation.
2. Hyper-Local Adaptability – Solutions are tailored to local constraints and opportunities.
3. Rapid Crisis Response – Culture of improvisation enables quick adaptation to disruptions.
4. Inclusive Growth – Engages and develops local suppliers and communities.
5. Sustainable Innovation – Naturally promotes resource conservation and circular thinking.
Implementation Roadmap
1. Identify “Constraint Hotspots” – Map where your supply chain faces the biggest resource, infrastructure, or cost constraints.
2. Launch Jugaad Challenges – Run internal and supplier competitions to solve specific problems with limited budgets (e.g., “Reduce packaging weight by 40% with under $500 investment”).
3. Create a Jugaad Toolkit – Develop simple guidelines for ethical improvisation (what’s allowed, what’s not) and share best practices across teams.
4. Celebrate & Reward Frugal Innovation – Recognize employees and suppliers who deliver clever, low-cost solutions.
5. Build Local Innovation Ecosystems – Partner with universities, startups, and informal sector networks to source Jugaad solutions.
Caveats & Balance
Jugaad must be guided by ethical boundaries and quality guardrails. It is not about cutting corners that compromise safety, ethics, or long-term value. The goal is frugal ingenuity, not reckless improvisation.
When balanced with robust governance, Jugaad transforms from a survival tactic into a strategic capability — enabling companies to operate profitably in volatile environments while building extraordinary resilience from the ground up.
Final Thought
In an era of constant disruption and resource constraints, Jugaad moves supply chain thinking from “How do we optimize perfect conditions?” to “How do we thrive in imperfect reality?” It cultivates the entrepreneurial spirit at every level of the supply chain, turning constraints into catalysts for innovation.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Wabi-Sabi philosophy?
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Wabi-Sabi philosophy?
08.01.2025
Integrating the Japanese Wabi-Sabi philosophy—centered on embracing imperfection, transience, and the beauty of the natural, weathered, and incomplete—into procurement and supply chain processes offers a profound counterpoint to modern industry’s obsession with flawless efficiency, hyper-optimization, and sterile predictability.
Wabi-Sabi teaches us to find value in authenticity, simplicity, and the graceful acceptance of limits and flux.
Core Principles of Wabi-Sabi in a Business Context
1. Imperfection is Inevitable & Informative – Flaws are not failures; they are evidence of nature, process, and uniqueness.
2. Nothing is Finished or Permanent – Everything is in a state of becoming or decay; processes should be adaptable and designs flexible.
3. Asymmetry & Irregularity – Natural, non-uniform patterns are more resilient and interesting than forced symmetry.
4. Simplicity & Austerity – Strip away the non-essential to reveal the true, functional essence.
5. Appreciation of the Weathered & Weathered – Value signs of use, repair, and the patina of time; they tell a story of journey and resilience.
Practical Application to Procurement & Supply Chain
1. Supplier Relationships: Embracing Human & Natural Imperfection
- Value Authenticity Over Polished Presentations – Choose suppliers who are transparent about their limitations and challenges, not just those with flawless marketing. A supplier who openly discusses their water scarcity challenges may be a more authentic, improvement-focused partner.
- Long-Term “Weathering” Together – View supplier relationships as evolving and maturing over time, gaining strength from shared history and recovered disruptions (like the repaired cracks of kintsugi).
- Asymmetric Partnerships – Not all relationships need to be perfectly balanced or identical. Nurture deep, collaborative partnerships with a few key suppliers (embracing their unique, “imperfect” capabilities) alongside a broader, simpler network for flexibility.
2. Inventory & Planning: Accepting Flux and Incompleteness
- Forecasting as a “Living Practice,” Not a Perfect Science – Acknowledge the inherent impossibility of perfect forecasts. Build adaptive, human-in-the-loop planning systems that respond to flux gracefully, rather than punishing planners for “inaccurate” predictions.
- Buffer as “Breathing Space” – Instead of seeing safety stock as waste, view it as the essential “negative space” (a key Wabi-Sabi concept) that allows the system to breathe and absorb shocks naturally.
- Manage by Exception & Nuance – Don’t seek to control every SKU with the same rigid, perfect algorithm. Allow human judgment to handle the unique, the irregular, and the exceptional items.
3. Quality & Materials: The Beauty of the Natural & Unfinished
- Source for Character & Story – In select product lines, intentionally source materials that show natural variation (e.g., undyed wool, wood with visible grain, leather with scars). This tells a story of authenticity that consumers value.
- Design for Patina & Repair – Procure components that age gracefully and are easily repairable. This shifts the focus from “like-new” perfection to long-term character and ownership.
- Accept “Good Enough” Functional Quality – For non-critical components, specify acceptable performance ranges rather than untenably tight tolerances. This reduces cost, waste, and supplier stress without compromising end-use.
4. Process Design: Simplicity, Austerity, and Human Touch
- Simplify Relentlessly – Apply the principle of austerity (koko) to processes. Audit procurement workflows and strip away redundant approvals, unnecessary reports, and over-engineered IT systems. Seek elegant, minimal process solutions.
- Value the “Artisan” in the System – Recognize and elevate the role of experienced buyers, planners, and logistics experts whose tacit knowledge and intuition (honed over time) handle nuance better than any algorithm. Their expertise is the “patina” of the process.
- Make Imperfections Visible & Informative – Instead of hiding process breakdowns, display them on andon boards or in team huddles as opportunities for mindful reflection and gentle improvement (kaizen in a Wabi-Sabi spirit).
5. Logistics & Delivery: The Poetry of Transience
- Embrace “Good Enough” Routing – Optimize transportation not for theoretical perfection, but for robust, flexible solutions that accommodate real-world variability (traffic, weather, driver availability).
- Use Return Loops & Packaging Cycles – See the beauty in circular, reusable packaging systems that gain character with each trip. A scratched but sturdy returnable container is more beautiful in its purpose than a pristine, single-use box.
- Accept the Patina of Use – In fleet management, maintain vehicles for safety and function, but don’t stress over minor aesthetic wear. It evidences a life of valuable service.
Example: A Furniture Company Applying Wabi-Sabi
- Procurement: Sources wood from forests practicing sustainable thinning, specifically selecting wood with knots, burls, and natural color variations as a mark of authenticity, not a defect to be hidden.
- Inventory: Keeps a modest stock of “character” wood for custom pieces, accepting that it is a finite, transient resource that will create unique, non-repeatable products.
- Design & Manufacturing: Builds furniture using joinery that allows for wood movement and future disassembly/repair. Offers a visible kintsugi-inspired repair service for damaged pieces.
- Quality Control: Trains inspectors to distinguish between structural flaws (which are rejected) and natural character marks (which are celebrated and documented for the customer).
- Team Mindset: Planning meetings begin with a reflection on a recent “imperfection” or unexpected event, discussing what it reveals about the system’s true nature and what can be learned—without blame.
Contrast with Traditional Models
- Traditional Lean/Six Sigma: Seeks to eliminate variation and defects, pursuing a state of sterile, controlled perfection.
- Wabi-Sabi-Inspired: Seeks to understand, harmonize with, and find value in natural variation and imperfection. It aims for robust, adaptive, and meaningful systems, not flawless ones.
Strategic Advantages of a Wabi-Sabi Supply Chain
1. Resilience Through Acceptance – By designing for flux and imperfection, the system becomes inherently more adaptable to shocks.
2. Reduced Waste & Stress – Eliminates the enormous cost and energy spent chasing the last 1% of “perfection” in forecasts, specifications, and efficiency.
3. Authentic Brand Narrative – Provides a powerful, genuine story of craftsmanship, sustainability, and mindful consumption.
4. Enhanced Innovation – Freedom from the tyranny of “perfect” allows for experimentation with asymmetric, simple, and unconventional solutions.
5. Human-Centric Work Culture – Reduces burnout by valuing wisdom and judgment over robotic precision, and by accepting that human processes are beautifully imperfect.
Implementation Steps
1. Reframe “Failure” – Lead a cultural shift to view deviations and surprises as sources of information and beauty, not merely failures.
2. Conduct a “Simplicity Audit” – Identify the most over-engineered, complex, or stressful process in procurement/supply chain and challenge teams to design a simpler, more forgiving version.
3. Launch a “Wabi-Sabi Pilot” – Choose one product line or supplier relationship to operate under new principles: accept natural material variations, build in flexible timelines, and document the story.
4. Develop New Aesthetic & Functional Standards – Co-create with designers and suppliers new guidelines that define the “beautifully acceptable” range for materials and processes.
5. Celebrate “Kintsugi Moments” – Publicly recognize and reward teams who beautifully recover from a disruption, leaving the system stronger and with a visible “seam of gold.”
Final Reflection
A Wabi-Sabi supply chain does not advocate for sloppiness or low standards. It advocates for wisdom in distinguishing between a harmful defect and a beautiful imperfection; between rigid fragility and flexible resilience.
It reminds us that supply chains are living, human-driven systems existing in a natural world of cycles, decay, and rebirth. By embracing asymmetry, transience, and rustic simplicity, we can build networks that are not only more robust and sustainable but also more humane and meaningful. The goal shifts from building a perfect machine to nurturing a vibrant, adaptive ecosystem that ages with grace and character.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Ubuntu philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Ubuntu philosophy?
07.01.2025
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Sisū philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Sisū philosophy?
06.01.2025
Integrating the Finnish concept of Sisū (pronounced see-soo)—the inner strength, grit, and relentless perseverance in the face of overwhelming adversity—into procurement and supply chain processes offers a powerful framework for building extreme resilience, adaptability, and a culture of tenacity.
Unlike philosophies focused on balance or comfort, Sisū is about action, fortitude, and pushing through the impossible with quiet determination.
Core Principles of Sisū in a Business Context
1. Resilience Beyond Measure – The ability to endure and recover from severe setbacks.
2. Action-Oriented Grit – Not just enduring, but proactively pushing forward against odds.
3. Mental Toughness & Perseverance – Sustaining effort despite fatigue, failure, or ambiguity.
4. Silent Determination – Less talk, more doing; solving problems without fanfare.
5. Adaptability in Crisis – Transforming obstacles into opportunities through sheer will.
Practical Application to Procurement & Supply Chain
1. Supplier Relationships: Forged in Adversity
- Select for Resilience, Not Just Cost – Choose suppliers who have demonstrated their own sisū—survived crises, innovated under constraint, shown ethical grit. Audit not just for compliance, but for crisis character.
- Co-develop Contingency Plans with Grit – Work with key suppliers to create “unbreakable” protocols for black-swan events. Test them under simulated extreme stress (e.g., cyber-attack drills, sudden sanctions, natural disasters).
- Long-Term “All-Weather” Partnerships – Commit to suppliers who stay with you through volatility, rewarding loyalty and shared perseverance over opportunistic switching.
2. Inventory & Risk Strategy: The Preparedness of Sisū
- Strategic Redundancy as a Mindset – Hold critical buffers not as waste, but as determined preparedness. Identify single points of failure and build resilient alternatives—even if they cost more.
- Transparency and Honesty About Vulnerabilities – Foster a culture where teams can flag extreme risks without blame, then tackle them with collective grit.
- Decentralized Stocking for Autonomy – Empower regional teams to hold survival stock for local contingencies, trusting their on-ground sisū to manage it wisely.
3. Logistics & Crisis Response: The Action of Sisū
- Develop “First-Responder” Logistics Networks – Pre-qualify backup carriers, charter options, and unconventional routes. Train logistics teams in crisis decision-making under pressure.
- Embrace Extreme Flexibility – When a port shuts down, a sisū-inspired team doesn’t just wait—they reroute through smaller ports, use rail, break bulk, and work around the clock to keep goods moving.
- Invest in Low-Tech Redundancies – Sometimes grit means having a low-tech fallback when high-tech systems fail (e.g., paper-based tracking, local radio networks for coordination).
4. Team Culture & Mindset
- Train for Mental Toughness – Use stress inoculation: simulations, war games, and scenario planning that push teams to their limits in a controlled environment.
- Celebrate “Grit Stories,” Not Just Success Stories – Recognize teams who fought through a supply crisis, even if the outcome wasn’t perfect. Honor effort, ingenuity, and perseverance.
- Lead with Calm Determination – Leaders model sisū by staying focused and resilient during disruptions, avoiding panic, and projecting steadfast resolve.
5. Sustainable Grit: Endurance for the Long Haul
- Build Physical & Digital Durability – Source components and choose IT systems not just for efficiency, but for ruggedness and longevity. Favor repairability over disposability.
- Invest in Supplier Development in Tough Regions – Sometimes sisū means helping a strategic supplier in an emerging market overcome local infrastructural hurdles—building roads, securing power—to create an unshakeable partner.
- Promote Well-being to Sustain Grit – True sisū is not about burnout. It’s about cultivating deep reserves. Encourage recovery, mental health support, and work-life balance so teams can tap into their fortitude when truly needed.
Example: An Electronics Manufacturer Applying Sisū
- Supplier Selection: Chooses a ruggedized component supplier from a Nordic country known for surviving economic crises, rather than the cheapest Asian option. They pay a premium for supplier resilience.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies a rare-earth mineral dependency. Instead of accepting the risk, the procurement team relentlessly pursues a recycling partnership and funds a startup exploring alternatives—a 10-year sisū project.
- Disruption Response: When a hurricane halts shipping, the logistics team works 72 hours straight, coordinating airlifts from three alternate airports, communicating via satellite phones when networks fail.
- Team Culture: Quarterly “stress tests” where teams are given an impossible supply chain problem to solve in 4 hours. No bonuses for winning—just respect for the grit shown.
Contrast with Other Philosophies
- Lagom (Balance): “Find the right amount.”
Sisū (Grit): “Endure any amount, and push beyond.” - Hygge (Comfort): “Create cozy security.”
Sisū (Grit): “Operate effectively in discomfort.” - Ikigai (Purpose): “Find joy in being.”
Sisū (Grit): “Find strength in persisting.”
Sisū complements these—it’s the backbone that upholds balance, protects comfort, and serves purpose when the world gets tough.
Implementation Roadmap
1. Crisis Audit – Identify past breakdowns and ask, “Did we show sisū? Where did we break?”
2. Define “Grit Metrics” – Track recovery time from disruptions, supplier survival rates, employee resilience scores.
3. Train for Tenacity – Invest in crisis leadership programs, mental toughness workshops, and scenario-based drills.
4. Reward Resilience – Include sisū behaviors in performance reviews: “How did you handle a major setback this year?”
5. Communicate the Philosophy – Share stories of Finnish sisū (Winter War, etc.) to embed the concept in culture.
The Strategic Advantage of a Sisū Supply Chain
In an age of constant disruption—pandemics, climate events, trade wars, cyber-attacks—a supply chain built on sisū transforms vulnerability into durability. It becomes:
- Unbreakable by design – because it’s prepared to bend and not snap.
- A talent magnet – for problem-solvers who thrive on challenge.
- A competitive moat – because competitors with fragile, efficiency-only chains will fail in crises where your sisū-chain persists.
- Ultimately more sustainable – because what endures wastes less.
Sisū reminds us that the goal is not just to avoid failure, but to build the inner fortitude to withstand, adapt, and advance no matter what the world throws at the supply chain. It’s not a tactic, but a cultural DNA—the quiet confidence that when all else fails, your people and processes will find a way through.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Hygge philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Hygge philosophy?
05.01.2025
Integrating the Hygge (pronounced “hoo-ga”) philosophy—the Danish concept of coziness, comfort, connection, and mindful well-being—into procurement and supply chain processes may seem abstract at first, but it offers a powerful human-centric lens to build trust, resilience, and quality into the backbone of a business.
Here is how a company can embed Hygge’s core principles into procurement and supply chain design.
Core Principles of Hygge in a Business Context
1. Atmosphere & Comfort – Creating a warm, safe, pleasant environment.
2. Presence & Mindfulness – Being in the moment, focusing on the human experience.
3. Togetherness & Trust – Nurturing genuine relationships and shared experiences.
4. Simplicity & Moderation – Avoiding overcomplication, appreciating the ordinary.
5. Gratitude & Contentment – Finding satisfaction in what you have and who you work with.
Practical Application to Procurement & Supply Chain
1. Supplier Relationships: From Transactions to “Hygge Partnerships”
- Long-term, cozy relationships over short-term gains – Choose suppliers you genuinely enjoy working with, who share values of fairness and well-being. Visit them, share meals, build personal connections (togetherness).
- Fair negotiations – Aim for agreements where both sides feel respected and comfortable, not squeezed. A Hygge negotiation seeks mutual contentment, not one-sided victory.
- Transparent communication – Create open, blame-free channels for dialogue—like a “cozy virtual fireside chat” regular check-in instead of just rigid performance reviews.
2. Work Environment for Procurement & Planning Teams
- Physical & digital workspace comfort – Ensure procurement teams have pleasant, calming workspaces (natural light, plants, warm lighting). Reduce stressful, frantic digital dashboards; design analytics tools that are clear, simple, and helpful.
- Mindful meetings – Start supplier or internal meetings with a personal check-in. Encourage presence—no multi-tasking. Perhaps even have a virtual “coffee/tea together” moment.
- Celebrate small wins – Acknowledge successful deliveries, resolved issues, or positive supplier feedback with small rituals (e.g., a team cake, a thank-you note). Gratitude strengthens bonds.
3. Process Design: Simple, Robust, and Stress-Reducing
- Simplicity in systems – Avoid over-engineered, complex approval workflows. Create processes that are intuitive and reduce anxiety—like clear guidelines, fewer bureaucratic steps.
- Buffer as comfort – Unlike extreme lean/JIT, incorporate reasonable buffers in inventory or lead times to reduce stress on teams and suppliers. This is the supply chain equivalent of having a cozy blanket for a cold night—it provides comfort and security.
- Predictable rhythms – Establish steady, predictable ordering cycles where possible, so suppliers can plan comfortably. Chaos and constant firefighting are anti-Hygge.
4. Quality & Sustainability: The Comfort of Good Conscience
- Source materials that feel good – Prioritize sustainable, ethically sourced materials that align with the comfort of knowing you’re doing good. This enhances brand atmosphere for the end customer too.
- Products that last and comfort – In procurement for product-based companies, choose components that ensure durability and quality—creating a sense of long-term contentment for the user.
- Local sourcing where possible – Shorter, more personal supply chains often align with Hygge’s emphasis on community and trust. Knowing your local supplier personally adds togetherness.
5. Logistics & Delivery: A Calm, Reliable Experience
- Stress-free delivery for partners – Offer flexible but clear delivery windows for carriers, treat drivers with warmth (provide a comfortable waiting area, refreshments).
- Packaging that feels good – Use simple, aesthetically pleasing, and functional packaging—unboxing should evoke a sense of care, not frustration with excess plastic and complexity.
- Transparency for customers – Provide clear, honest tracking without overpromising. Under-promise and over-deliver to create a feeling of reliable comfort.
Example: A Furniture Company Applying Hygge
- Procurement: Sources wood from a family-owned Nordic forest supplier they’ve visited regularly. They negotiate fair prices allowing the supplier to invest in worker well-being.
- Planning: Keeps a moderate buffer of popular fabric rolls to avoid last-minute panic and allow designers creative freedom.
- Team Culture: The planning team starts Mondays with a 15-minute coffee chat to share weekend highlights. They have candles (LED for safety) and soft lighting in their office.
- Logistics: Uses unbleached recycled paper packaging that is simple to open. Delivery drivers are offered a hot drink in winter during pickup.
- Supplier Relationships: Hosts an annual “Hygge Supplier Day” with shared lunch, feedback sessions, and collaborative planning in a relaxed setting.
Contrast with Traditional Models
- Traditional: Emphasizes cost, speed, efficiency, often at the expense of human elements.
- Hygge-Inspired: Emphasizes trust, comfort, simplicity, and mutual well-being as foundations for long-term efficiency and resilience.
Benefits of a Hygge-Inspired Supply Chain
1. Enhanced Supplier Loyalty & Innovation – Suppliers treated as cozy partners will go the extra mile, share ideas, and prioritize your needs during shortages.
2. Reduced Team Burnout – A calm, pleasant work environment increases retention and reduces errors caused by stress.
3. Greater Resilience – Trust-based relationships and buffers provide natural shock absorbers during disruptions.
4. Brand Alignment – For consumer-facing brands, a supply chain rooted in care and comfort can be a authentic storytelling point.
5. Sustainable by Nature – Simplicity, local focus, and ethical sourcing align with environmental and social goals.
Implementation Steps
1. Start with the team – Introduce Hygge principles internally. Create cozy spaces and rituals.
2. Map “moments of stress” in the procurement cycle and redesign them for comfort—e.g., painful RFP processes, chaotic inbound logistics.
3. Choose one key supplier relationship to transform using Hygge principles—deepen communication, express gratitude, negotiate with well-being in mind.
4. Incentivize differently – Reward procurement staff for relationship quality and sustainability metrics, not just cost savings.
5. Measure cultural metrics – Supplier satisfaction scores, team well-being, reduced emergency orders.
Final Thought
Hygge in supply chain is not about adding fluffy blankets to warehouses (though it doesn’t hurt). It’s about designing processes and relationships that create a sense of security, trust, and human warmth. In a world of volatility and transactional pressure, a Hygge-inspired supply chain can become a rare competitive advantage: a resilient, humane network where people genuinely want to work together, fostering quality and innovation naturally.
It’s the art of making the heart of operations feel like a safe, welcoming hearth rather than a cold, relentless machine.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Lagom philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Lagom philosophy?
04.01.2025
Integrating the Swedish concept of Lagom (pronounced lah-gom), meaning “not too little, not too much” or “just the right amount,” into procurement and supply chain processes offers a profound shift towards balanced, sustainable, and resilient operations.
Lagom is fundamentally about moderation, fairness, sustainability, and collective well-being. It rejects excess, waste, and aggressive optimization at the expense of people or the planet.
Here is how a company can build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Lagom philosophy:
Core Principles of Lagom in Supply Chain
1. Balance & Moderation: Avoid extremes. Not just-in-time to the point of fragility, not overstocked to the point of waste.
2. Sustainability & Resourcefulness: Use only what is needed. Design for longevity and minimal waste.
3. Fairness & Equity: Treat all partners (suppliers, employees, communities) with respect and fairness.
4. Functionality & Quality: Prioritize “fit for purpose” and durability over flashy excess.
5. Collective Good: Decisions should benefit the entire ecosystem, not just the company’s bottom line.
Practical Application Across the Supply Chain
1. Strategic Sourcing & Supplier Selection
- “Just the Right” Partners: Move beyond price-only auctions. Select a balanced portfolio of suppliers—a mix of large (for scale) and small/local (for resilience and community benefit).
- Fair Relationships: Negotiate for fair prices that allow suppliers a healthy margin to invest in their workers and innovation. This is the opposite of squeezing them to the last penny.
- Long-term Collaboration: Prefer fewer, deeper partnerships (Lagom number) over a vast, fragmented base. This fosters trust, quality, and joint problem-solving.
- Transparency: Share forecasts and challenges appropriately, seeking a balanced view of risk and opportunity.
2. Inventory & Demand Planning
- “Just the Right” Inventory: Employ demand-sensing and advanced forecasting to avoid both stockouts and bloated warehouses. Aim for the balanced point where service level costs and holding costs are in equilibrium.
- Buffer Stock as a Thoughtful Choice: Hold moderate, strategic buffers for critical items, not as waste, but as a prudent investment in resilience (a Lagom buffer).
- Embrace Circularity: Design processes for repair, refurbishment, and take-back. This is the ultimate “not too much” for raw material extraction.
3. Logistics & Transportation
- Right-Sized Shipping: Optimize container and truckload fill rates to be “just full”—maximizing space without overloading. Consolidate shipments.
- Balanced Modal Mix: Choose the most appropriate (not just the fastest or cheapest) transport mode. Could a slower sea freight be “just right” for the environmental cost saved?
- Green Logistics: Invest in electric vehicles or carbon offset programs to achieve a “balanced footprint”—neutralizing the unavoidable impact.
4. Packaging & Materials
- Minimalist, Functional Packaging: Use the minimum material required to protect the product. Innovate with reusable, returnable, or compostable packaging.
- Design for Disassembly: Source and design products so components can be easily separated and recycled at end-of-life.
5. Performance Metrics (KPIs)
Shift from extreme, single-focus KPIs to a balanced scorecard:
- Instead of only: “Minimize Purchase Price Variance”
- Add: “Supplier Sustainability Score,” “Payment Terms Fairness,” “Innovation Ideas Co-developed.”
- Balance: Cost, Quality, Speed, Resilience, Sustainability, and Partnership Health.
6. Internal Culture & Process
- Avoid Burnout: Reject a “hero culture” of constant fire-fighting. Staff teams adequately (Lagom workload) for sustainable performance.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Empower local teams to make “right amount” decisions that fit their context, within a framework of guiding principles.
- Mindful Consumption: Internally promote a culture of questioning every purchase request: “Is this necessary? Is this the right amount? Can we use something we already have?”
Visual Model: The Lagom Supply Chain
A Lagom supply chain would look less like a hyper-lean, global race and more like a balanced, regional network:
- Sourcing: Prioritized nearshoring for a balanced risk/cost profile.
- Inventory: Strategic hubs with moderate, optimized stock levels.
- Transport: A mix of modes chosen for total impact (cost + carbon + time).
- Relationships: Long-term, open-book partnerships with key suppliers.
Example: A Furniture Company Applying Lagom
- Procurement: Sources sustainably harvested wood from regional forests (not lowest-cost, global), paying a fair price to support sustainable forestry.
- Design: Creates modular, repairable furniture with minimal, biodegradable packaging.
- Inventory: Keeps core components in stock for quick assembly and repair, but assembles to order.
- Logistics: Uses hybrid electric trucks for last-mile delivery on optimized routes.
- End-of-Life: Offers a take-back program to refurbish or recycle products.
Contrast with Traditional Models
- Traditional Lean/JIT: “Minimize waste, maximize efficiency.” (Can lead to fragility and supplier squeeze).
- Lagom Balanced: “Optimize for resilience, fairness, and sustainability within efficient boundaries.”
Conclusion: The Lagom Advantage
Building a procurement and supply chain on Lagom isn’t about sacrificing profitability. It’s about achieving balanced, long-term prosperity.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced Resilience from balanced buffers and strong partnerships.
- Risk Mitigation through sustainable and ethical practices.
- Brand Trust & Loyalty from conscious consumers.
- Employee Engagement from meaningful, fair work.
- Sustainable Cost Structure through waste reduction and resourcefulness.
Ultimately, a Lagom supply chain is a mature supply chain—one that recognizes that true efficiency is not about relentless minimization, but about finding the “just right” point for all stakeholders: the company, its people, its partners, and the planet.
AI Procurement. How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Ikigai philosophy?
AI Procurement
How can a company build its procurement and supply chain processes using the Ikigai philosophy?
03.01.2025
AI Procurement. Top Procurement Courses and Training Worldwide
AI Procurement
What are the best courses and training available in the world for procurement professionals?
02.01.2025
The best procurement training depends heavily on your career stage, specialization, and region. The global landscape offers a mix of prestigious academic degrees, industry-recognized certifications, and elite executive programs. Here’s a breakdown of the top-tier options, categorized for clarity.
1. Premier Global Certifications (Industry-Standard)
These are the most portable and recognized credentials worldwide.
CIPS (Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply): The global gold
standard, especially in the UK, Commonwealth, and Europe. It is a progressive
qualification from Level 2 to Level 6, culminating in MCIPS (Member). Many
global job descriptions list MCIPS as a requirement.
o Best for: Professionals seeking a comprehensive, globally recognized career
passport in procurement and supply chain.
ISM (Institute for Supply Management) – CPSM/CPSD: The leading authority
in North America. The Certified Professional in Supply Management
(CPSM) is highly respected and focuses on strategic sourcing, finance, and
supply management.
o Best for: Professionals operating in or with North American markets,
emphasizing strategic and financial acumen.
APICS (Association for Supply Chain Management) – CSCP/CPIM: While
broader than procurement, the Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP) is
immensely valuable for procurement leaders who need deep integration with the
end-to-end supply chain.
o Best for: Procurement professionals aiming for executive roles where
understanding the full supply chain is critical.
2. Elite Academic & Executive Education
For deep strategic knowledge and networking.
Master’s Degrees:
o MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics (MS in Supply Chain
Management): Arguably the world's top program, with a focus on analytics,
technology, and innovation.
o University of Cambridge – Master of Studies (MSt) in Supply Chain
Leadership: A part-time, modular program for senior professionals, combining
Cambridge’s academic rigor with practical leadership.
o Michigan Ross (Master of Supply Chain Management), Pennsylvania State
University (Smeal), and other top-tier business schools offer excellent
specialized master’s or MBAs with strong procurement concentrations.
Executive Short Courses:
o Harvard Business School (HBS): Offers executive programs like ‘Driving
Strategic Impact: Leading Procurement & Supply Chain
Transformation’ Unparalleled for high-level strategy and leadership.
o INSEAD: Programs like ‘Strategic Procurement in the Digital Age’ focus on
innovation and global strategy.
o Kellogg School of Management (Northwestern): Renowned for Executive
Strategies for Supply Chain Management.
o University of Oxford (Saïd Business School): Courses like ‘Oxford
Programme on Negotiation’ are legendary for procurement leaders.
3. Specialized & Technology-Focused Training
For modern procurement challenges.
Digital Procurement & AI:
o Procurement Leaders / World Commerce & Contracting: Offer courses
on digital transformation, AI in procurement, and advanced analytics.
o Suppliers platforms (like Coupa, SAP Ariba, Jaggaer): Vendor-specific
certifications on Source-to-Pay (S2P) platforms are highly valuable for
operational roles.
Negotiation Mastery:
o The Gap Partnership: Their ‘Advanced Negotiation Programme’ is world-
famous in corporate circles for its strategic methodology.
o Scotwork: Another global leader in negotiation training with a strong track record.
Legal & Contracting:
o World Commerce & Contracting (formerly IACCM): The Certified
Commercial Contracts Manager (CCCM) is the benchmark for contract
management excellence.
4. Leading Online Learning Platforms
For flexible, skill-specific advancement.
Coursera / edX: Host courses from MIT (MicroMasters in Supply Chain),
Rutgers, and ISM. Excellent for foundational and intermediate knowledge.
LinkedIn Learning & Udemy: For tactical skill-building (e.g., ‘Excel for
Procurement’, ‘Introduction to Strategic Sourcing’).
How to Choose: A Strategic Guide
1. For Early-Career Professionals (1-5 years):
o Start with CIPS Level 4/5 or ISM CPSM. They provide a solid foundation. Use
platforms like Coursera for prerequisites.
2. For Mid-Career Managers (5-10 years):
o Complete your MCIPS or CPSM. Pursue specialized training in negotiation
(Gap Partnership) or digital tools. Consider an APICS CSCP to broaden your
perspective.
3. For Senior Leaders & Directors (10+ years):
o Aim for executive education at HBS, INSEAD, or Oxford to build peer networks
and strategic vision. These are for leadership, not just technical skills.
4. For Specialists:
o Category Management: Look for specialized courses from Procurement
Leaders or The Faculty (Australia/Asia).
o Data Analytics: Seek courses in Python, SQL, and spend analytics (via data
science platforms or Coursera).
o Sustainable Procurement: CIPS and ISM now have dedicated modules and
certificates on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance).
Final Recommendation:
The Unbeatable Combination: MCIPS (CIPS) + an executive program from a
top-10 business school. This gives you the technical credibility and the strategic
leadership pedigree.
Consider Your Geography: CIPS is stronger in Europe/Asia, ISM in the
Americas. Choose accordingly.
Invest in Networking: The value of programs like HBS or INSEAD often lies as
much in the peer group you join as in the curriculum.
Always check: Does the program offer practical tools, recognized certification, and
a strong alumni network? The "best" course is the one that aligns with your next
career move and fills your most critical skill gaps.
AI Procurement. How can AI be used in the field of procurement?
AI Procurement
How can artificial intelligence be used in the field of enterprise procurement?
01.01.2025
Artificial Intelligence is fundamentally transforming enterprise
procurement from a tactical, administrative function into a strategic, predictive, and autonomous powerhouse. Its applications span the entire Source-to-Pay (S2P) lifecycle.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how AI is being used in enterprise procurement:
1. Strategic Sourcing & Supplier Management
Intelligent Sourcing & Market Analysis: AI algorithms can scan thousands of
websites, news feeds, and databases to monitor commodity prices, geopolitical risks,
and supply market trends in real-time. This provides predictive insights for optimal
buying timing.
Supplier Discovery & Onboarding: AI can automatically identify and qualify new
suppliers from global databases, analyze their financial health, news sentiment, and
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) credentials, drastically reducing onboarding
time.
Supplier Risk Management: AI provides continuous, predictive risk monitoring. It can
flag suppliers at risk of bankruptcy, operational disruption (using weather/social data), or
compliance issues (sanctions, regulatory changes) long before traditional methods.
Automated RFx & Auction Analysis: AI can help structure RFPs, evaluate complex
bid responses (even parsing unstructured text), and suggest optimal award scenarios
beyond just price, considering risk, innovation, and total cost of ownership.
2. Spend Analytics & Cost Optimization
Spend Classification & Cleansing: Machine Learning (ML) models automatically
cleanse and classify 100% of spend data (from messy PO descriptions, invoices) into
accurate, unified categories. This creates a "single source of truth" for spend visibility.
Anomaly Detection & Fraud Prevention: AI identifies patterns indicative of fraud,
maverick spending, or duplicate invoices by comparing transactions against historical
data and defined rules (e.g., purchases just below approval thresholds, unusual vendor
changes).
Predictive Cost Modeling & Should-Cost Analysis: AI models predict future price
points of components/materials based on factors like raw material indices, labor rates,
and demand forecasts, giving procurement powerful negotiation leverage.
3. Procurement Process Automation &Efficiency
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA): Combines RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
with AI to handle complex, judgment-based tasks:
o Touchless Invoice Processing: Computer Vision (OCR++) reads invoices, ML
matches them to POs and delivery receipts, and AI resolves discrepancies—all without
human intervention.
o Automatic Contract Management: NLP (Natural Language Processing) extracts key
clauses (SLAs, termination dates, price escalators) from thousands of contracts,
flagging risks and non-standard terms.
Cognitive Procurement Assistants (Chatbots): AI-powered chatbots handle routine
queries from employees and suppliers, freeing up staff for strategic work.
4. Contract Management & Compliance
Smart Contract Authoring: AI suggests optimal clauses based on category, risk
profile, and jurisdiction, ensuring compliance with company standards.
Obligation Management: AI monitors contract repositories and operational data to
ensure both parties meet obligations (e.g., volume commitments, rebates, innovation
workshops).
Renewal & Opportunity Alerts: AI predicts contract renewal dates and analyzes
spend to recommend consolidation, renegotiation, or switching opportunities.
5. Procurement in the Supply Chain
Predictive Demand Sensing & Inventory Procurement: AI links procurement directly
to the supply chain by predicting demand spikes/slumps more accurately than traditional
forecasts. This triggers autonomous, just-in-time procurement orders to optimize
inventory costs.
Logistics & Shipping Optimization: AI optimizes freight and logistics procurement by
analyzing routes, carrier performance, and costs in real-time.
The Underlying AI Technologies Powering This:
Machine Learning (ML): For pattern recognition, prediction, and classification.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): For understanding contracts, emails, and
specifications.
Computer Vision: For reading documents, invoices, and even monitoring supplier
facilities via satellite imagery.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): For executing the repetitive tasks AI dictates.
Tangible Benefits for the Enterprise:
Cost Savings: 5-15%+ beyond traditional methods through predictive analytics and
optimization.
Efficiency Gains: Up to 50-70% reduction in manual processing time.
Risk Reduction: Proactive identification of supply, financial, and compliance risks.
Strategic Impact: Frees procurement teams to focus on innovation, supplier
collaboration, and value creation.
Improved Compliance: Enforces policy automatically and provides complete audit
trails.
Challenges & Considerations:
Data Quality: ‘Garbage in, garbage out.’ AI requires clean, integrated data from ERP,
finance, and supply chain systems.
Change Management: Requires reskilling procurement professionals from tactical
buyers to strategic data interpreters and relationship managers.
Ethics & Bias: AI models must be audited to avoid perpetuating bias in supplier
selection.
Integration: Must work seamlessly within existing procurement tech stacks (ERP, S2P
suites like SAP Ariba, Coupa, etc.).
The Future: Autonomous Procurement
The end state is ‘Self-Optimizing Supply Networks.’ AI will not just recommend
actions but will autonomously execute routine procurement—placing orders, negotiating
spot buys, managing supplier risk—within pre-defined strategic guardrails set by
humans.
In summary, AI in procurement moves the function from being reactive and
administrative to being predictive, prescriptive, and ultimately autonomous. It is
the core technology enabling Chief Procurement Officers to become true strategic
partners to the business.
ActiveNature Season 12. Water World

ActiveNature Season 12. Water World
2024
Interesting and rare moments of everyday life on the water surface.
Nature
Season 12. Past Bonus
Baikal, Blue Lagoon, Dead Sea, Jordan River, Pamukkale, Strokkur
Season 16. Future Bonus
Season 18. Future Bonus
Durmitor, Everest, Himalayas, Tara River Canyon
| Activity | Hobby |
| Thermal springs swimming | Archery |
| Mud wrap | Collecting |
| Helicopter flight | Poker |
| Electric scooter | Reading |
| Electric moped | Table tennis |
| Bike | 3D modeling |
| Car | Website development |
| Roller coaster | Smart contract development |
| Tyrolean traverse | Radio controlled car |
| Skiing | App development |
Season 1. Bonus.
City Insight
Belarus: Turov, Zaslavl, Zhitkovichi
Season 2. Bonus.
City Insight
Andorra: Andorra la Vella
Bosnia and Herzegovina: Sarajevo
France: Blagnac, Rennes, Toulouse
Germany: Bonn, Cologne, Dusseldorf
Greece: Bogetici, Chania, Fira, Firostefani, Oia, Thessaloniki
Malta: Birgu, Cospicua, Floriana, Senglea, Valletta
Montenegro: Kolasin, Niksic, Podgorica, Zabljak
Northern Cyprus: Kyrenia, Nicosia
Romania: Bucharest
Slovakia: Bratislava
Slovenia: Ljubljana
Event Insight
Sport: Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games, Spa-Francorchamps 2024 Formula 1 Belgium Grand Prix, Spa-Francorchamps 2024 Porsche Mobil 1 Supercup
Place Insight
National Parks: Biogradska Gora, Durmitor, Plitvice Lakes
Heritage: Mont-Saint-Michel, Santorini
Resorts: Canopy by Hilton Zagreb City Centre, Ibis Orly Rungis, Park Inn by Radisson Danube Bratislava, Pullman Cologne, W Barcelona, Westin Zagreb
Wildlife: Tara River Canyon
Season 3. Bonus.
Place Insight
Resorts: Crowne Plaza Istanbul Old City IHG Hotel, Holiday Inn Istanbul Old City IHG Hotel, Renaissance Istanbul Polat Bosphorus Hotel
Season 4. Bonus.
City Insight
China: Guangzhou
Laos: Phonsavan, Thanon Tha, Vientiane
Myanmar: New Bagan, Nyaung-U, Old Bagan, Yangon
Nepal: Bhaktapur, Kathmandu, Lalitpur, Lukla, Pheriche
Vietnam: Ho Chi Minh, My Tho
Place Insight
Heritage: Bagan, Plain of Jars
Resorts: Excelsior Yangon, Fairfield by Marriott Kathmandu, Four Points by Sheraton Guangzhou Baiyun, Grand Hotel Saigon
Wildlife: Everest, Himalayas, Mekong
Season 12. Past Bonus
Place Insight
Wildlife: Blue Lagoon, Strokkur
Stats: Countries 13 (88), Cities 50 (440), Events 3 (65), Places (HandMade+Nature) 26 (101), Activity 10 (20), Hobby 10 (20)
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Interchain Messaging”
In this course, you will learn how to build cross-L1 Solidity dApps with Interchain Messaging and Avalanche Warp Messaging.
Course Content
Interoperability
In the first section, we cover some basic concepts of interoperability in multi-chain systems. You will learn about examples of interoperability between blockchains and the terms “source,” “destination,” and “message.”
Avalanche Interchain Messaging
In this section, we learn what Avalanche Interchain Messaging is and what is abstracted away from the general dApp developer. You will also build your first cross-L1 dApps.
Securing Cross-Chain Communication
In this section, we look at techniques to secure cross-chain communication. We dive into signature schemes, multi-signature schemes, and the BLS multi-signature scheme.
Avalanche Interchain Messaging Protocol
Avalanche blockchains can natively interoperate between one another using AWM. You will learn about the AWM message format and how the message flow works.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, students will:
- Understand the challenges of cross-chain communication
- Know what separates Avalanche Warp Messaging from other cross-chain communication protocols
- Understand the differences between Avalanche Warp Messaging and Teleporter
- Apply their knowledge by building cross-Avalanche L1 dApps, such as asset bridges
Topics
- Interoperability between blockchain
- Source, Message and Destination
- Recap of Multi-Chain Networks
- Interoperability in Multi-Chain Systems
- Finality Importance in Interoperabile Systems
- Trusted Third Parties
- Avalanche Starter Kit
- Initial Setup
- Close and Reopen Codespace
- Getting Test Tokens
- Contract Development with Foundry
- Interchain Messaging Basics
- ICM Basics
- Recap of Bytes, Encoding and Decoding
- Sending a Message
- Sender Contract
- Receiving a Message
- Receiver Contract
- Send a Message
- Adapt the contract
- Two-Way Communication
- Sender Contract
- Create the Sender Contract
- Receiver Contract
- Create the Receiver Contract
- Send a Roundtrip Message
- Adapt the Contracts
- Invoking Functions
- Encoding of multiple Values
- Create Simple Calculator Sender
- Create Simple Calculator Receiver
- Call simple Calculator
- Encoding the Function Name
- Extend the Calculator
- Interchain Messaging Registry
- How the ICM Registry works
- Interact with the ICM Registry
- Retrieving Interchain Messenger from the Registry
- Verify if Sender is Interchain Messaging
- Avalanche Warp Messaging
- Recap P-Chain
- Warp Message Format
- AWM Relayer
- Dataflow
- Message Pickup
- Message Delivery
- Load Considerations
- Trust Assumptions
- Running a Relayer
- Relayer Introduction
- Configuration Breakdown
- Configure & Run Relayer
- Restricting-the-relayer
- Restricting a Relayer
- Allowed Relayer
- Incentivizing a Relayer
- Incentivizing a Relayer
- Fee Data Flow
- Determining the Fee
- Setting Incentives
- Deploy Fee Token Contract
- Incentivize an AWM relayer
- Interaction Flow With Fees
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Interchain Token Transfer”
In this course, you will learn how to transfer assets across multiple Avalanche blockchains with Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer ICTT.
Course Content
Getting Started with Interchain Token Transfer
In this section, you will learn how to use our Interchain Token Transfer toolbox to perform cross-chain operations. We’ll guide you through the process of using our user-friendly interface to deploy contracts, create bridges, and transfer assets across the testnet chains (Fuji C-Chain, Echo, and Dispatch).
Tokens and Token Types
In this section, you will learn about the different types of tokens that can be transferred between Avalanche blockchains. We will cover ERC-20 and native tokens and how to deploy and transfer them using our toolbox. Furthermore, you will learn what wrapped native tokens are and how they can be used to transfer assets between chains.
Token Bridging
Next we will talk about the high level concepts of token bridging and demonstrate how to use our toolbox to create and manage bridge contracts for cross-chain transfers between the testnet chains.
Interchain Token Transfer Architecture
In this chapter we will look at the design of Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer. You will learn about the file structure of the contracts and the concepts of the token home and token remote.
ERC-20 to ERC-20 Bridge Implementation
You will learn how to use our toolbox to deploy ERC-20 tokens and create bridges to transfer them between the testnet chains.
Multi-Chain Token Operations
Here you will learn about the concept of multi-hops and how to use our toolbox to bridge tokens between multiple testnet chains.
Native to ERC-20 Bridge Implementation
In this chapter you will learn how to use our toolbox to bridge a native token as an ERC-20 token to another testnet chain.
Send and Call Operations
In this chapter you will learn how to use our toolbox to call smart contracts with the tokens after sending them to another testnet chain.
Cross-Chain Token Swaps
In this chapter you will learn how to perform cross-chain token swaps between the testnet chains using our toolbox.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, you will:
- Understand what Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer is and when to use it.
- Understand the different options for transferring assets between multiple chains.
- Be able to deploy tokens and create bridges using our toolbox.
- Be able to perform cross-chain token transfers between testnet chains using our toolbox.
- Apply the knowledge gained in the course by enabling assets to be transferred between multiple Avalanche blockchains.
Topics
- Tokens
- Native Tokens
- Transfer Native Tokens
- Transfers and Smart Contract
- ERC-20 Tokens
- Deploy and Transfer an ERC-20 Token
- ERC-20 and Smart Contracts
- Wrapped Native Tokens
- Create a Wrapped Native Token
- Token Bridging
- Bridge Architecture
- Use a Demo Bridge
- Bridge Hacks
- Interchain Token Transfer
- Avalanche Interchain Token Transfer
- Interchain Token Transfer Design
- File Structure
- Token Home
- Token Remote
- ERC-20 to ERC-20 Token Bridge
- ERC-20 to ERC-20 Bridge
- Deploy an ERC-20
- Deploy a Home Contract
- Deploy a Remote Contract
- Register Remote Bridge
- Transfer Tokens
- Integrate ICTT with Core
- Deploy Your Own ICTT Frontend
- ERC-20 Multi-Hop Transfer
- Overview of Multi-hop Transfers
- Deploy Token Remote for Multi-hop
- Register Remote Bridge
- Multi-hop Transfer
- Native to ERC-20 Token Bridge
- Native to ERC-20 Token Bridge Overview
- Deploy Native Token Home
- Deploy ERC20 Token Remote
- Register Remote Bridge
- Native Token Bridge Transfer
- Send and Call
- Introduction
- Send and Call Receivers
- Mock Receivers
- Deploy a Mock Receiver
- Cross-Chain Token Swaps
- Wrap Exchange Contract
- Deploy Wrapped Exchange Contract
- Scaling Token Decimals
- Scaling with TokenRemote
- Example USDC as Native Token (DIY)
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “L1 Tokenomics”
This course is designed to give you a deep understanding of tokenomics, including the creation, distribution, utility, and governance of tokens within blockchain ecosystems. By the end of this course, you will have practical skills in managing tokens across multi-chain ecosystems, configuring transaction fees, and designing staking and governance models.
Course Content
Basics
Learn the fundamentals of tokenomics, including native tokens, ERC-20 tokens, wrapped tokens, and how token decimals affect transactions and supply.
Native Tokens
Explore how to create custom native tokens, use Avalanche’s native token minter, and integrate ERC-20 tokens as native tokens in cross-chain environments.
Multi-Chain Ecosystems
Delve into interchain token transfers and cross-chain functionality, using both ERC-20 and native tokens across multiple blockchains.
Staking
Understand staking tokens, liquid staking, and how to deploy staking contracts, with a focus on post-Etna upgrade features.
Transaction Fees
Master transaction fee configuration, dynamic fee models, and learn how to distribute fees effectively within decentralized ecosystems.
Token Distribution
Learn about initial token allocation, advanced vesting schedules, bonding curves for token pricing, and how to implement airdrops.
Governance
Study governance models, DAOs, quadratic voting, and the latest innovations in governance (Governance 2.0) for decentralized decision-making.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, you will:
- Gain a solid grasp of token fundamentals, tokenomics models, and how to create sustainable token economies.
- Learn how to create custom native tokens and integrate ERC-20 tokens as native tokens in multi-chain environments.
- Understand the challenges and opportunities in cross-chain token transfers, and liquidity management.
- Master the technical aspects of configuring transaction fees, setting up staking contracts, and designing dynamic fee models.
- Create initial allocation plans, implement advanced vesting schedules, and manage bonding curves and airdrops.
- Develop governance structures, including DAOs and quadratic voting models, to manage decentralized decision-making effectively.
Topics
- Basics
- Native Tokens
- ERC-20 Tokens
- Deploy and Transfer an ERC-20 Token
- Wrapped Native Tokens
- Deploy and Interact with Wrapped Token
- Token Decimals
- Advanced Native Tokens
- Custom Native Tokens
- Configure Custom Native Tokens
- Native Token Allocation
- Activating Native Minter Precompile
- Native Minter Precompile
- Use ERC-20 as Native Token
- Multi-Chain Ecosystems
- Introduction
- Interchain Token Transfers
- Use ERC-20 as Native Token (DIY)
- Use any Native as Native Token (DIY)
- Cross-Chain Liquidity Pools
- Quiz Time
- Staking
- Introduction
- Liquid Staking
- Staking Contract (post Etna Upgrade)
- Registering PoS Validators
- Transaction Fees
- Introduction
- Transaction Fee Configuration
- Dynamic Fee Configuration
- Fee Distribution
- Token Distribution
- Initial Allocation
- Vesting Schedules
- Bonding Curves
- Airdrops
- Governance
- Introduction
- Governance Models
- DAOs
- Quadratic Voting
- Governance 2.0
- Conclusion
Completion Certificate
Avalanche Academy
Avalanche Academy
Course “Avalanche Fundamentals”
This online course introducing you to the exciting world of the Avalanche technology! This course will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the basic concepts making Avalanche unique.
Throughout, you’ll learn the key features and benefits of the platform, plus how to build on it. You can also ask our expert instructors questions.
By the end of these courses, you’ll have the knowledge and skills to leverage the power of blockchain technology for your own projects and applications. We’re excited to have you join us on this journey and can’t wait to see what you’ll create with Avalanche!
By the end of this course, you will:
- Understand how Avalanche consensus works and what makes it different.
- Understand how Avalanche L1s enable scalability, customizability, and independence.
- Understand the Primary Network, a special Avalanche L1, and how to interact with it.
- Understand how Virtual Machines enable developers to create more optimized and capable blockchain systems and to tackle completely new use cases unachievable with previous solutions.
You can evaluate your own understanding of the material through quizzes and claim a certificate for successful completion at the end.
Overall, this course aims to provide a foundational understanding of Avalanche. By completing it, you will be better prepared to take on more advanced courses focused on building on Avalanche.
Topics
- Avalanche Consensus
- Consensus Mechanisms
- Snowman Consensus
- Throughput vs. Time to Finality
- Multi-Chain Architecture
- Avalanche L1s
- Features & Benefits of Avalanche L1s
- Avalanche9000 Upgrade
- Avalanche L1s vs Layer 2
- Set Up Core Wallet
- Use Dexalot L1
- Creating an L1
- Connect & Fund Core Wallet
- Network Architecture
- Create a Blockchain
- Set up Validator Nodes
- Convert a Subnet to an L1
- Test your L1
- Remove Node
- Introduction in Interoperability
- Source, Message and Destination
- ICM, ICM Contracts & ICTT
- BLS Signature Schemes
- Use a Signature Scheme
- Multi-Signature Schemes
- Use Multi-Signature Schemes
- BLS Signature Aggregation
- Use Cases
- Introduction to VM Customization
- VM Configuration
- VM Modification
- VM Creation
- Permissioning
- Compliance
- Transaction Allowlist
- Activate Transaction Allowlist
- Contract Deployer Allowlist
- Activate Contract Deployer Allowlist
- Permissioning Validators
- Private Blockchains
- Intain Markets Case Study
CERTIFICATE OF COMPLETION
Cardano Academy
Cardano Academy
Certification “Cardano Blockchain Certified Associate” (CBCA)
Module 1 Overview
Introduces the foundation of blockchain, from the main components of a typical blockchain network, to how consensus algorithms provide a mechanism to reach agreement in decentralized systems. It delves into the Byzantine Generals’ Problem and explains what Byzantine and Practical Byzantine fault-tolerant systems are. This module looks at the key concepts behind proof-of-work and proof-of-stake systems, including their respective limitations. Other proof-based consensus models including proof of authority, proof of Importance and proof of History are briefly explored. Encryption methods are examined and how hash functions and digital signatures provide data authenticity and integrity.
Topics
- Introduction to Blockchain
- Consensus Algorithms
- The Byzantine Generals Problem (BGP)
- The Basics of Networks
- Properties of Consensus Algorithms
- The Original Bitcoin Whitepaper
- BFT vs. PoW Consensus Algorithms
- Blockchain Fundamentals
- Components and Structure of a Blockchain
- Blockchain Careers and Use Cases
- Blockchain Generations: First and Second
- Introduction to Ethereum
- Ethereum’s Decentralized Systems
- Third Blockchain Generation
- Cardano’s Native Token
- Blockchain Architecture: Layer 1
- Blockchain Types
- Evolution of the Internet
- Understanding Encryption and Decryption
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Attack Models
- Hash Function
- Avalanche Effect
- Resistance
- Types of Hash Functions
- Hash Function Applications
- Signing and Verification Algorithms in Digital Signatures
- The Digital Signature Verification Algorithm Under Attack
- Wallets in a Blockchain Network
- Hot and Cold Storage
- Introduction to Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Synchrony
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Vote-Based Consensus
- Introduction to Proof-Based Consensus
- Proof of Work
- Proof of Stake
- Different Stakeholders’ Approaches to Proof of Stake
- Proof of Authority (PoA)
- Proof of Activity (PoA)
- Proof of Importance (PoI)
- Proof of Burn (PoB)
- Proof of Capacity (PoC)/Proof of Space (PoSpace)
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)
- Proof of Contribution (PoCo)
- Proof of History (PoH)
Module 2 Overview
Builds on the concepts introduced in Module 1. It defines the transaction models used in blockchain, including account-based, Unspent Transaction Output, and extended Unspent Transaction Output. It examines the content of a block and the role of the block producer. Module 2 also explains how the risks against double-spending and Sybil attacks are mitigated, the causes of soft and hard forks, and the importance of incentive mechanisms. It concludes with a look at layer 1 and layer 2 scaling solutions.
Topics
- Introduction to Transaction Models
- Tokens
- The Transaction Lifecycle
- Record-Keeping Transaction Models
- The UTxO Transaction Model
- Inputs, Outputs and Wallets
- A Blockchain’s State
- Cardano’s Extended UTxO
- The EUTxO model
- Introduction to the Basics of Block Structure
- Longest Chain Algorithms
- Sending and Receiving Transactions via Block Producing Nodes
- Blockchain Miners
- Blockchain Parameters
- The Fundamental Properties of Blockchain
- Double-Spending Attack Example
- Block Generation Power
- Avoiding Double-Spending Attacks
- Soft Fork and Hard Fork
- Introduction to Blockchain Incentives
- Why Blockchain Needs Incentives
- Rewards in Proof-of-Work Protocols
- Types of Networks in Blockchain
- Acquiring Tokens in Mainnet and Testnet
- API and Nodes Communication Protocol
- Nebula’s Architecture
- Introduction To Scalability
- Fundamentals
- Scalability Techniques: Part 1
- Scalability Techniques: Part 2
- Scalability Techniques: Part 3
- Introduction to Layer 2 Solutions
- State Channels
- Drawbacks of State Channels
- Rollups
- Drawbacks of Rollups
- Other Scaling Solutions
Module 3 Overview
Focuses on the Cardano blockchain, it describes Cardano’s genesis and genesis entities, and the mission and principles governing Cardano. It looks at the Cardano node and how the eras have developed and enhanced features of the network. Ouroboros, Cardano’s consensus algorithm, is examined, along with the reward and incentive mechanism of Cardano. The governance process including Cardano Improvement Proposals is explained, along with the role of the Cardano Community.
Topics
- Introduction to Cardano Genesis
- Cardano’s Principles
- Cardano Genesis
- Cardano Roadmap
- Introduction to Cardano Architecture
- Cardano Eras: Part 1
- Cardano Eras: Part 2
- Networking
- Consensus in Public Permissionless Ledgers
- Ouroboros: a Family of Consensus Protocols
- The Ouroboros Family: Classic, Praos and Genesis
- Ouroboros: Crypsinous, Chronos, Leios, BFT and Omega
- Delegated Proof of Stake
- Rewards Sharing Scheme (RSS): Part 1
- Rewards Sharing Scheme (RSS): Part 2
- Wallets
- BIPs and CIPs
- Types of Addresses
- Payment Addresses
- Stake Addresses
- Fundamentals
- Programming on Cardano
- Smart Contract Languages
- Embedded Domain Specific Languages (eDSL)
- Why Does Community Matter?
- Decentralization
- What Does Community Offer?
- Why Cardano?
- Community Groups: Part 1
- Community Groups: Part 2
- History
- Cardano Improvement Proposals
- The CIP Process
- The CIP Actors
- Notable CIPs: Part 1
- Notable CIPs: Part 2
Module 4 Overview
Looks at how to get started buying, storing, and transferring ada. It also examines how staking works on Cardano with the staking lifecycle, along with the role of stake pools and stake pool operators. It describes how to create and transfer both native assets and non-fungible tokens and concludes with a look at decentralized applications and exchanges.
Topics
- Smart Contract Programming Frameworks
- API Query Layers
- Other Tools and Services
- Blockchain Explorers
- Choosing a Wallet
- Getting Started With Your Chosen Wallet
- Buying ADA from a Centralized Exchange (CEX)
- Transactions
- Staking on Cardano
- Stake Pool Operators (SPOs)
- How to Choose a Stake Pool?
- Cardano Foundation Delegation Strategy
- Alice and Bob Q&A
- Chimeric Ledger
- Staking Lifecycle: GUI vs CLI
- Jargon Buster
- Metadata Standards
- Creating a Native Token
- Wallets and DApps Interactions
- DApp Tour: Part 1
- DApp Tour: Part 2
- DApp Tour: Part 3
- Future of DApps on Cardano
- Security and Standards
Practice Exam
Web 3.0 Procurement. Chainlink Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Chainlink Ecosystem
Chainlink is a blockchain abstraction layer that enables universally connected smart contracts. Through a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink allows blockchains to securely interact with external data feeds, events and payment methods, providing the critical off-chain information needed by complex smart contracts to become the dominant form of digital agreement.
The Chainlink Network is driven by a large open-source community of data providers, node operators, smart contract developers, researchers, security auditors and more. The company focuses on ensuring that decentralized participation is guaranteed for all node operators and users looking to contribute to the network.
Tokenized assets
Reliable and automated data integration. Attach any type of financial data to tokenized assets and automate updates to increase investor transparency and reduce manual efforts.
Automated compliance. Meet regulatory requirements and internal policies by embedding compliance solutions directly into tokenized assets.
Faster market entry with scalable infrastructure. Accelerate time-to-market and increase global access by securely connecting across any public or private blockchain with a single integration.
Enable digital asset mobility. Seamless connectivity between blockchains and traditional finance. Easily integrate traditional financial systems with blockchains to increase liquidity and market accessibility for institutions and protocols alike.
Real-time data synchronization. Keep tokenized assets updated with real-time valuations and compliance data to support seamless, real-time markets as assets move across chains.
Privacy and security for institutional transactions. Support secure, private cross-chain transactions that protect financial data while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Streamline post-trade operations. Atomic settlement. Create payment-versus-payment (PvP) and delivery-versus-payment (DvP) workflows onchain while mitigating counterparty risks.
Enhanced operational efficiency. Automate post-trade processes to reduce settlement delays, reconciliation errors, and operational costs.
Automated and efficient risk management. Add real-time risk monitoring, automated compliance, and smarter collateral management to transactions to reduce exposure as assets move from one party to another.
StableCoins
Market confidence. Enhance credibility with institutions by building on stablecoin infrastructure recognized across global capital markets for its security, reliability, and operational maturity.
Automated compliance. Support seamless regulatory compliance across jurisdictions with real-time policy enforcement, secure identity management, and streamlined monitoring and reporting.
Secure interoperability. Unlock multi-chain stablecoin distribution through Chainlink’s enterprise-grade interoperability standard, enabling greater market reach without introducing fragmentation risk.
End-to-end reliability. Prevent downtime and disruption with battle-tested infrastructure that supports stablecoin operations at scale.
Operational transparency. Ensure visibility into reserves backing stablecoins with infrastructure that makes reserve validation available onchain.
DeFi utility. Protocols and investors prefer to only list, integrate, and support assets with verifiable backing, enhancing liquidity.
Data-driven minting logic. Anchor stablecoin issuance to real-world asset values for high-integrity operations.
Proof of Reserves enforcement. Accelerate the growth of ecosystems with infrastructure designed to scale securely as networks mature.
Controlled stablecoin issuance. Enforce collateral thresholds, allowlist access, and issuance rules to ensure stablecoins are compliant.
Ecosystem liquidity unlocked. Preferred by DeFi and institutional protocols, making it easier for stablecoins to integrate into high-liquidity environments and access built-in demand.
Blockchain-agnostic movement. Facilitate stablecoin transfers across different blockchain environments with secure delivery and consistent logic.
Seamless value exchange across markets. Move stablecoins between fragmented liquidity venues and infrastructure layers without integration friction or operational overhead.
Programmable transfer logic. Embed transfer conditions directly into smart contracts to automate controls such as allowlisting, rate limits, and jurisdiction-aware routing.
Payment settlement. Use trusted exchange rates and secure messaging to settle stablecoin payments between currencies quickly and at low cost.
Interoperability with global financial infrastructure. Seamlessly settle transactions using existing payment rails, from market infrastructures to fintech platforms.
Compliance focused. Automatically apply sanctions screening, jurisdiction rules, and audit logging to stablecoin transfers at the point of settlement.
DeFi
Most decentralized and secure. Chainlink oracle networks are secured by node operators running security-audited software that has been rigorously validated to operate at scale without downtime or corruption.
Highest quality data, resistant to manipulation. Data is sourced from multiple premium, authenticated APIs that are aggregated into a final validated answer, removing any single point of failure.
Most widely adopted oracle network in DeFi. The Chainlink Network helps secure tens of billions of dollars within the DeFi ecosystem by connecting hybrid smart contracts with high-quality data and offchain computation.
Rapid integration and deployment. Developers can rapidly build, test, and deploy advanced DeFi applications that leverage multiple external resources using pre-built and reliable decentralized services.
A diverse range of decentralized services. Chainlink powers numerous decentralized services, including Data Feeds, Proof of Reserve, Automation, Verifiable Randomness Function, and Cross-Chain Interoperability.
Blockchain-agnostic oracle networks. Developers building DeFi applications have access to external data and computation across all leading smart contract-enabled blockchain networks to support multi-chain development.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Binance Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Binance Ecosystem
BNB is the native coin of the BNB Chain ecosystem, essential for powering its multifaceted Web3 environment. It supports transactions on the BNB Smart Chain (BSC), the opBNB L2s, and BNB Greenfield . Besides transaction fees, BNB serves as a governance token, granting holders the ability to participate in the BNB Chain’s decentralized on-chain governance.
Additionally, BNB functions as a strategic reserve asset and plays a critical role in the BNB Executive Total Value Locked (TVL) campaign, driving ecosystem growth and incentivizing adoption.
Real World Assets Tokenization
Real World Assets (RWAs) in crypto involve tokenizing physical assets like real estate, receivables, and loans on blockchain. Tokenizing real-world assets (RWAs) involves converting ownership rights of physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. It provides liquidity for your tangible assets and creates better cash flow for you.
BNB Chain Payment Solution
Still trying to figure out how to integrate BNB Chain payment gateways into your business? Still confused about where you could spend your cryptos? You come to the right place.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Avalanche Ecosystem
Avalanche is a layer one blockchain that functions as a platform for decentralized applications and custom blockchain networks. It is one of Ethereum’s rivals, aiming to unseat Ethereum as the most popular blockchain for smart contracts. It aims to do so by having a higher transaction output of up to 6,500 transactions per second while not compromising scalability.
This is made possible by Avalanche’s unique architecture. The Avalanche network consists of three individual blockchains: the X-Chain, C-Chain and P-Chain. Each chain has a distinct purpose, which is radically different from the approach Bitcoin and Ethereum use, namely having all nodes validate all transactions. Avalanche blockchains even use different consensus mechanisms based on their use cases.
After its mainnet launch in 2020, Avalanche has worked on developing its own ecosystem of DApps and DeFi. Different Ethereum-based projects such as SushiSwap and TrueUSD have integrated with Avalanche. Furthermore, the platform is constantly working on improving interoperability between its own ecosystem and Ethereum, like through the development of bridges.
Business & Consumer Applications
Avalanche accelerates blockchain business growth by enabling fast, scalable Web3 application development. The Avalanche network is a system of interconnected Layer 1 blockchains, linked through native Interchain Messaging. With built-in customizability and out-of-the-box tooling, projects on Avalanche can scale both up and across the network. Avalanche L1s offers tailored technology for real-world needs.
DeFi on Avalanche
Avalanche’s ultra-fast, low-latency network provides the building blocks for a scalable, efficient and cost-effective financial system on-chain. Avalanche supports everything from dynamic trading strategies to programmable stablecoins, while customizable Layer 1s (L1s) allow institutions to deploy tailored, compliance-aware environments.
Infrastructure on Avalanche
Avalanche is all about scalable and interoperable blockchains, facilitated by Avalanche’s native Interchain Messaging (ICM) feature. Avalanche is the multi-chain platform helping build a scalable Web3 universe—designed with precision control over execution, validation, and cross-chain interoperability. Interchain Messaging enables communication across the layer 1 multiverse for interoperability out-of-the-box.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Cardano Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Cardano Ecosystem
Cardano is a groundbreaking blockchain platform that uses proof-of-stake technology to create a more sustainable and accessible financial system. It stands out for its research-first approach and scientific philosophy, making it highly secure and energy-efficient. The platform aims to provide reliable financial services to everyone, including those currently without access to traditional banking. Since its inception, it has evolved into one of the leading blockchain platforms, processing millions of transactions while maintaining its commitment to sustainability and academic rigor.
Retail
Counterfeit goods pose a significant challenge to the global economy, causing financial losses, eroding brand reputation, and reducing customer trust. Cardano’s blockchain offers a tamper-proof solution to combat counterfeiting by providing secure, immutable systems for tracking product provenance and ensuring authenticity. Businesses can certify the originality of their products, enabling consumers to verify authenticity instantly and building confidence in the supply chain.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chains often lack transparency and efficiency, leading to counterfeit goods, poor quality control, and increased costs. Cardano’s blockchain enables real-time tracking and verification of goods. Companies can record every step of a product’s journey, from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and improving logistical processes.
Smart Contract
Cardano introduced smart contracts in 2021 and now supports the development and deployment of smart contracts using multiple different languages.
- Aiken – for on-chain validator scripts only: a language & toolchain favouring developer experience.
- Marlowe – a domain-specific language, it covers the world of financial contracts.
- opshin – a programming language for generic Smart Contracts based on Python.
- Plutus – a platform to write full applications that interact with the Cardano blockchain.
- plu-ts – Typescript-embedded smart contract programming language and a transaction creation library.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Polkadot Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Polkadot Ecosystem
Polkadot is an open-source sharded multichain protocol that connects and secures a network of specialized blockchains, facilitating cross-chain transfer of any data or asset types, not just tokens, thereby allowing blockchains to be interoperable with each other. Polkadot was designed to provide a foundation for a decentralized internet of blockchains, also known as Web3.
Polkadot is known as a layer-0 metaprotocol because it underlies and describes a format for a network of layer 1 blockchains known as parachains (parallel chains). As a metaprotocol, Polkadot is also capable of autonomously and forklessly updating its own codebase via on-chain governance according to the will of its token holder community.
Polkadot provides a foundation to support a decentralized web, controlled by its users, and to simplify the creation of new applications, institutions and services.
The Polkadot protocol can connect public and private chains, permissionless networks, oracles and future technologies, allowing these independent blockchains to trustlessly share information and transactions through the Polkadot Relay Chain (explained further down).
Polkadot’s native DOT token serves three clear purposes: staking for operations and security, facilitating network governance, and bonding tokens to connect parachains .
Smart Contract
Polkadot offers developers flexibility in building smart contracts, supporting both Wasm-based contracts using ink! (written in Rust) and Solidity contracts executed by the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine).
- Wasm (ink!) contracts – contracts are written in Rust and compiled to Wasm. The advantage of Wasm is that it allows for more flexibility, speed, and potentially lower execution costs compared to EVM, especially in the context of Polkadot’s multi-chain architecture
- EVM-compatible contracts – contracts are written in languages like Solidity or Vyper and executed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The EVM is widely standardized across blockchains, including Polkadot parachains like Astar, Moonbeam, and Acala. This compatibility allows contracts to be deployed across multiple networks with minimal modifications, benefiting from a well-established, broad development ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Algorand Ecosystem
Algorand is a self-sustaining, decentralized, blockchain-based network that supports a wide range of applications. These systems are secure, scalable and efficient, all critical properties for effective applications in the real world. Algorand will support computations that require reliable performance guarantees to create new forms of trust.
DeFi
Ultra-low transaction fees and instant finality make DeFi applications on Algorand accessible and highly efficient. Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism offers a secure and decentralized environment for DeFi applications. Bridge assets to and from Algorand through robust interoperability solutions, connecting Algorand to other blockchains and the outside world. Algorand is scalable by design, ensuring its DeFi protocols can handle high transaction fees without compromising speed or cost.
Tokenized real-world assets
Tokenization reduces reliance on intermediaries, lowering costs and streamlining operations. Tokenization opens up investments to broader audiences, promoting financial inclusion. Blockchain ensures clear ownership and transfer history for tokenized assets. Enhanced access through tokenization drives increased liquidity, making assets easier to trade.
Data traceability & tracking solutions
Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism fosters a secure and decentralized environment for data traceability and tracking applications. PPoS is built to scale—meaning it can handle high transaction throughput without compromising speed or cost. Algorand’s fast block time and instant finality translate to near real-time data traceability. This ensures updates are recorded quickly and irreversibly, offering a secure and trustworthy audit trail for tracked information. Algorand’s low transaction fees make it suitable for scenarios where frequent data tracking is required. This may be ideal for applications like supply chain management, where every step of a product’s journey needs to be documented.
Stablecoins, digital money & payment solutions
Transaction fees on Algorand are incredibly low at 0.001 Algo per transaction, making it a viable option for everyday purchases and microtransactions. Stablecoins on Algorand are accessible to all, even those without a bank account. Anyone in the world can set up a mobile crypto wallet and gain access. Algorand users can transact with price-stable assets, lowering cryptocurrency volatility concerns. Algorand’s Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism delivers a secure and decentralized environment for digital money and payment solutions. Algorand is scalable by design, ensuring applications can handle high transaction volume without compromising speed or cost. With custom smart contract support, Algorand enables developers to build innovative payment solutions and integrate them seamlessly with existing systems.
Smart Contracts
Algorand Smart Contracts (ASC1) are self-executing programs deployed on the Algorand blockchain that enable developers to build secure, scalable decentralized applications. Smart contracts on Algorand can be written in Algorand Typescript, Algorand Python, or directly in TEAL. Smart contract code written in Typescript or Python is compiled to TEAL, an assembly-like language that is interpreted by the Algorand Virtual Machine (AVM) running within an Algorand node.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
 Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Solana Ecosystem
Solana is a highly functional open source project that banks on blockchain technology’s permissionless nature to provide decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions. The Solana protocol is designed to facilitate decentralized app (DApp) creation. It aims to improve scalability by introducing a proof-of-history (PoH) consensus combined with the underlying proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus of the blockchain. Because of the innovative hybrid consensus model, Solana enjoys interest from small-time traders and institutional traders alike. A significant focus for the Solana Foundation is to make decentralized finance accessible on a larger scale.
Smart Contract
On Solana, “smart contracts” are called programs. Programs are deployed on-chain to accounts that contain the program’s compiled executable binary. Users interact with programs by sending transactions containing instructions that tell the program what to do.
Solana programs are predominantly written in the Rust programming language, with two common approaches for development:
Anchor: A framework designed for Solana program development. It provides a faster and simpler way to write programs, using Rust macros to reduce boilerplate code. For beginners, it is recommended to start with the Anchor framework.
Native Rust: This approach involves writing Solana programs in Rust without leveraging any frameworks. It offers more flexibility but comes with increased complexity.
Web 3.0 Procurement. Ethereum Ecosystem
Web 3.0 Procurement. Ethereum Ecosystem
Ethereum is a decentralized open-source blockchain system that features its own cryptocurrency, Ether. ETH works as a platform for numerous other cryptocurrencies, as well as for the execution of decentralized smart contracts.
Ethereum’s own purported goal is to become a global platform for decentralized applications, allowing users from all over the world to write and run software that is resistant to censorship, downtime and fraud.
DeFi
DeFi is an open and global financial system built for the internet age – an alternative to a system that’s opaque, tightly controlled, and held together by decades-old infrastructure and processes. It gives you control and visibility over your money. It gives you exposure to global markets and alternatives to your local currency or banking options. DeFi products open up financial services to anyone with an internet connection and they’re largely owned and maintained by their users. So far tens of billions of dollars worth of crypto has flowed through DeFi applications and it’s growing every day.
DAO
A DAO is a collectively-owned organization working towards a shared mission. DAOs allow us to work with like-minded folks around the globe without trusting a benevolent leader to manage the funds or operations. There is no CEO who can spend funds on a whim or CFO who can manipulate the books. Instead, blockchain-based rules baked into the code define how the organization works and how funds are spent. They have built-in treasuries that no one has the authority to access without the approval of the group. Decisions are governed by proposals and voting to ensure everyone in the organization has a voice, and everything happens transparently onchain.
Payments
While traditional financial institutions have built robust payment systems over decades, they often remain constrained by borders, working hours, and legacy infrastructure. Ethereum offers a new paradigm: a global, 24/7 financial platform that enables near-instant, programmable transactions for anyone with internet access.
Smart contract
A “smart contract” is simply a program that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. It’s a collection of code (its functions) and data (its state) that resides at a specific address on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts are a type of Ethereum account. This means they have a balance and can be the target of transactions. However they’re not controlled by a user, instead they are deployed to the network and run as programmed. User accounts can then interact with a smart contract by submitting transactions that execute a function defined on the smart contract. Smart contracts can define rules, like a regular contract, and automatically enforce them via the code. Smart contracts cannot be deleted by default, and interactions with them are irreversible.
The two most active and maintained languages are:
Solidity
- Object-oriented, high-level language for implementing smart contracts.
- Curly-bracket language that has been most profoundly influenced by C++.
- Statically typed (the type of a variable is known at compile time).
- Supports: Inheritance, Libraries, Complex user-defined types.
Vyper
- Pythonic programming language
- Strong typing
- Small and understandable compiler code
- Efficient bytecode generation
- Deliberately has less features than Solidity with the aim of making contracts more secure and easier to audit.
9th International Public Procurement Conference

9th International Public Procurement Conference
03.10 – 05.10.2024
Umm Al Quwain, United Arab Emirates
Tentative Program: IPPC9 Tentative Program.doc
Conference Program: IPPC9 Conference Program.doc
Prepared materials for the conference
Title: TENDER SYSTEM USING THE ETHEREUM BLOCKCHAIN PLATFORM: A PROCESS WITHOUT TRUST IN THE ORGANIZER
Paper Status: Accepted
Full paper: Full paper.doc


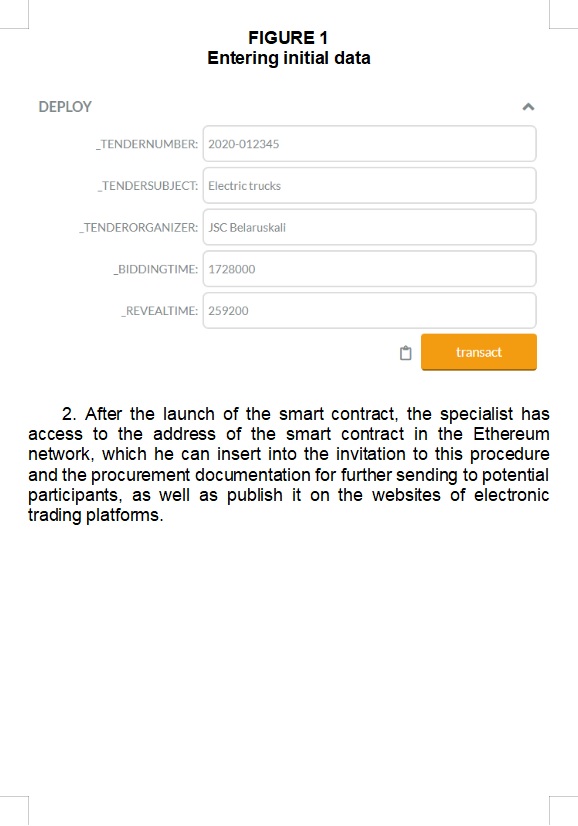
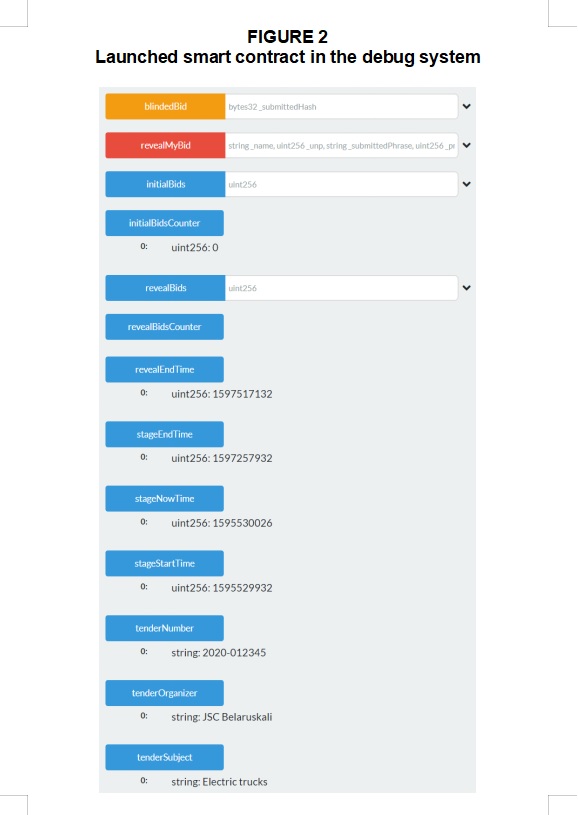

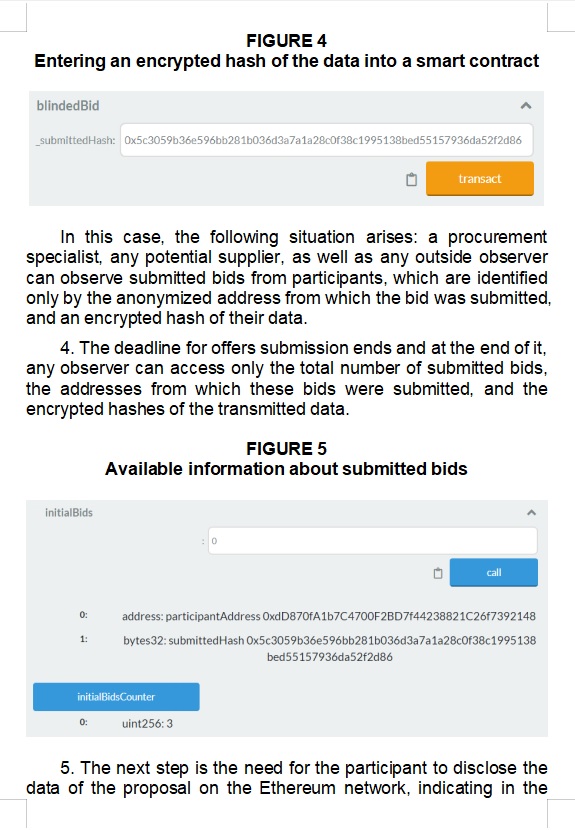

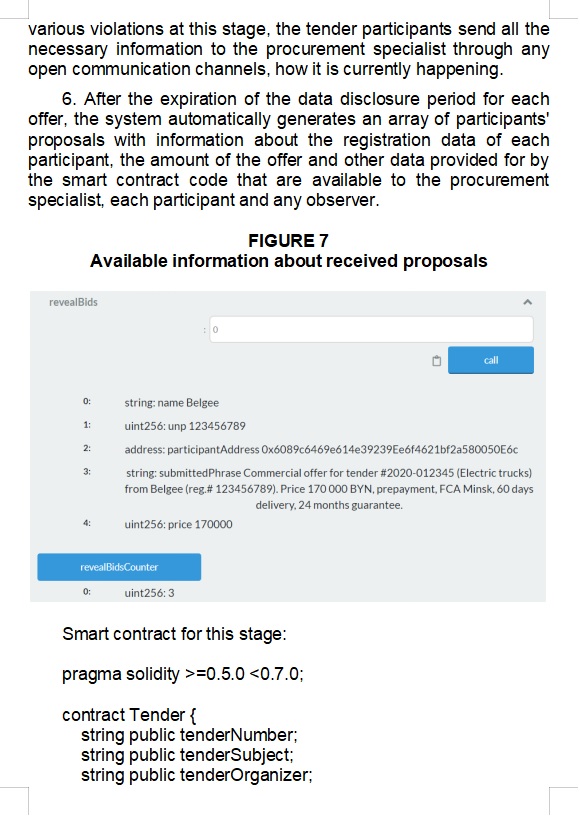




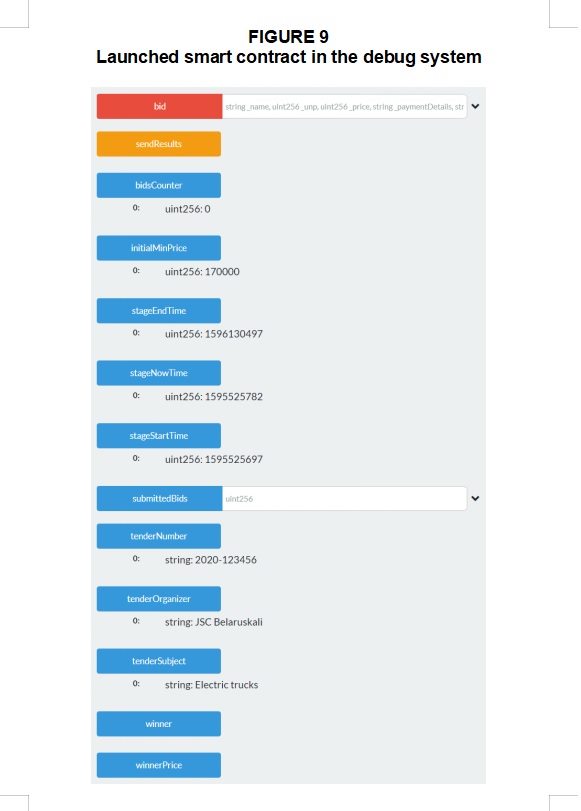
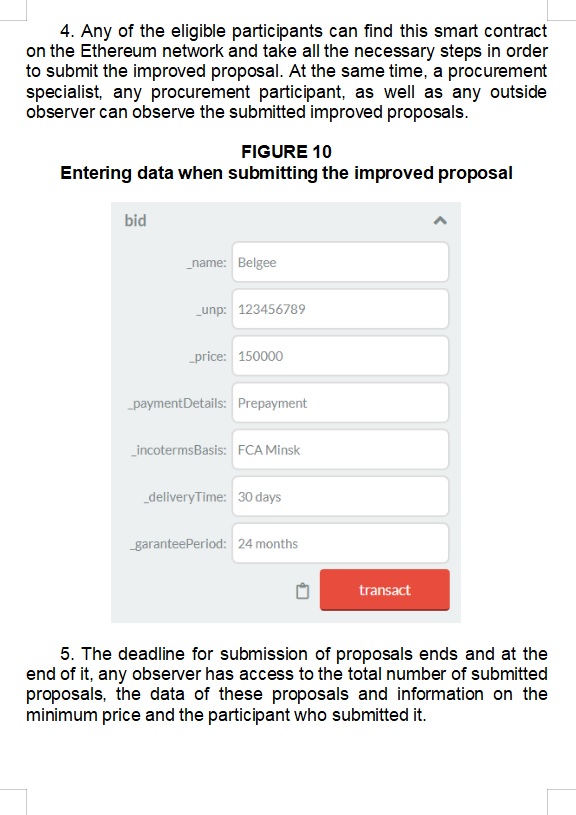
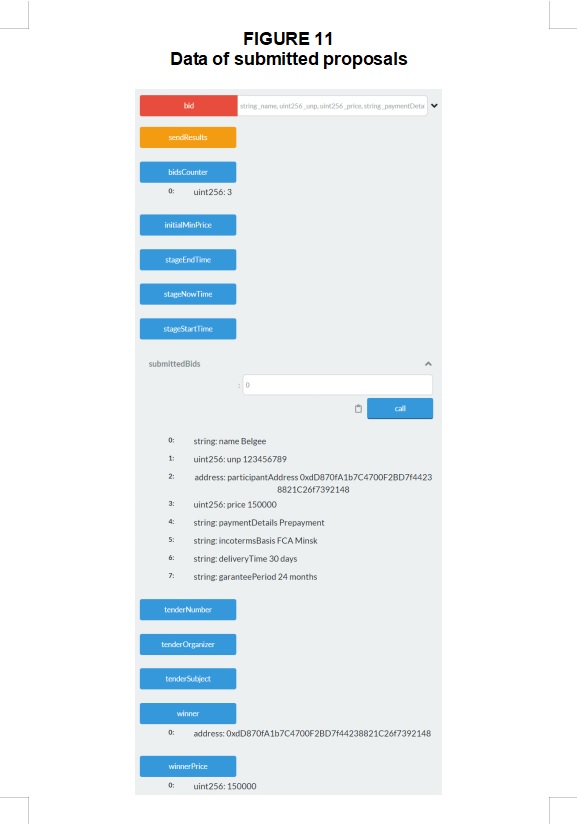





ActiveNature Season 11. Deep Blue

ActiveNature Season 11. Deep Blue
2023
Interesting and rare moments of everyday life of deep water dwellers.
Nature
Season 12. Future Bonus
Season 13. Future Bonus
Anse Source d’Argent, Seychelles beach
Season 14. Future Bonus
Chamarel Seven Colored Earth Geopark
Season 15. Future Bonus
Season 16. Future Bonus
Season 18. Future Bonus
| Activity | Hobby |
| Snorkeling | Wood puzzle |
| Scuba Diving | Quiz game |
| Swimming | Billiards |
| Fishing | Bowling |
| Rafting | Photography |
| Kayaking | Basketball |
| Pedal Catamaran | Tennis |
| Boat | Cooking |
| Gondola | Roulette |
| Manta swimming | Bookmaking |
Season 1. Bonus.
City Insight
Belarus: Alexandrovka, Belynichi, Berezino, Blon, Bobruisk, Bogushevich, Borisovshchina, Borovaya, Bragin, Brili, Buda-Kashalyova, Budslav, Bykhov, Chachersk, Chenki, Cherikov, Chojniki, Dobrenevo, Dobrush, Dovsk, Dukora, Dzerzhinsk, Fanipol, Gorki, Grudinovka, Ivianec, Kalinkovichi, Khalch, Khatyn, Korenovka, Korma, Krasny Bereg, Krichev, Lesnaya, Loshany, Loyev, Maly Trostenets, Maryina Gorka, Molodechno, Mozyr, Mstislavl, Narovlya, Osipovichi, Ozertso, Pralniki, Priluki, Pukhovichi, Rakov, Ratomka, Raubichi, Rogachev, Rubezhevichi, Selec, Shklov, Slavgorod, Smilovichi, Stankovo, Svetlogorsk, Sula, Vietka, Vileyka, Yelsk, Yurovichi, Zabrodie, Zhilichi
Russia: Ekaterinburg, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Podolsk, Serpukhov, Vladivostok, Yelizovo, Zaraysk
Tajikistan: Buston, Dushanbe, Istaravshan, Khujand
Event Insight
Auto: Auto Expo 2023, Belaz Fest 2023. Retro, Fire Service 170th anniversary 2023
Military: V-Day Parade 2023
Sport: Minsk 2023 Belarus Drag Racing Championship, Moscow 2023 Russian Drift Series, Raubichi 2023 Belarus Drift Championship
Place Insight
NatureStay: 01. 52.488142, 31.156243
Resorts: Kronon Park Hotel
Wildlife: Avacha Bay, Fann
Season 3. Bonus.
Place Insight
Resorts: Mövenpick Jumeirah Lakes Towers
Season 4. Bonus.
Event Insight
Show: Post Malone 2023, Robbie Williams 2023
Sport: Singapore 2023 Porsche Carrera Cup Asia, Singapore 2023 TSS The Super Series, Singapore 2023 Formula 1 Singapore Grand Prix
Place Insight
Resorts: Ramada Colombo
Season 7. Bonus.
City Insight
Kenya: Nairobi
Madagascar: Antananarivo, Antsirabe, Miandrivazo, Morondava
Mauritius: Bois Cheri, Curepipe, Pamplemousses, Port Louis
Seychelles: Beau Vallon, Cap Samy, La Digue, Pointe La Rue, Victoria
Place Insight
National Parks: Nairobi, Praslin
Resorts: Carlton Madagascar, DoubleTree by Hilton Seychelles Allamanda Resort and Spa, Radisson Blu Poste Lafayette Resort & Spa Mauritius, Savoy Seychelles Resort & Spa
Wildlife: Anse Source d’Argent, Baobab Avenue, Chamarel Seven Colored Earth Geopark, Kirindy Forest, Seychelles beach
Season 8. Bonus.
Place Insight
Heritage: Besakih, Borobudur, Goa Lawah, Penataran, Prambanan, Tanah Lot, Tirta Gangga
Resorts: Peninsula Bay Resort
Stats: Countries 5 (75), Cities 90 (390), Events 12 (62), Places (HandMade+Nature) 25 (75), Activity 10 (10), Hobby 10 (10)
Международная конференция “SMART TALER 2023”

Международная конференция “SMART TALER 2023”
20.05.2023
Отель Виктория «Олимп», Минск, Республика Беларусь + online
Международная конференция о трендах в fintech-сфере, майнинге, блокчейне и криптовалютах
Темы:
1 Тренды мировой криптоиндустрии в 2023-24 г.г.
2 Регулирование криптовалют на государственном уровне.
3 Внедрение блокчейн-технологий как бизнес-инструмент. Какие преимущества мы получаем.
4 Успешные кейсы криптостартапов. Как развить свой.
5 Риски инвестирования. Как не потерять свои деньги.
6 Оборудование и сервисы для эффективного майнинга в 2023-24 г.г.
7 Актуальные решения в блокчейн-разработке.
8 Практические кейсы в области финтех для бизнеса и банковского сектора.
9 Возможности платежных систем сегодня и их будущее.
10 Новые вызовы в безопасности личных данных, обслуживающих сервисов и в хранении активов.
Выступления:

Игорь Мамоненко
Генеральный директор группы компаний Belhard
Обзор криптовалютной сферы
– первая криптовалюта в Беларуси;
– единые валюты;
– вопросы коммерческой тайны при децентрализованных валютах;
– квантовые компьютеры;
– риски в криптомире.

Олег Огиенко
Директор компании BitRiver по взаимодействию с органами власти.
Перспективы развития криптомайнинга и энергоемких блокчейн вычислений в ЕАС
– когда криптовалюты станут новым инструментом внешнеэкономической деятельности;
– насколько тесно связано будущее цифровой экономики и криптомайнинга;
– какие положительные эффекты от развития промышленного майнинга ожидают финансовый и энергетический сектора России;
– почему криптомайнинг является основным двигателем науки и технологий.
Денис Смирнов
Блокчейн-консультант, исследователь криптовалют.
Субъективные оракулы и децентрализованное разрешение споров: ключ к развитию экосистемы DeFi
– краткое введение в Web3 и DeFi;
– важность децентрализованного разрешения споров в контексте Web3;
– точки Шеллинга как ключ к децентрализованному разрешению споров;
– доступные решения;
– возможные реализации и их перспективы.
Валерия Федякина
СЕО холдинга Bitmama в Катаре.
Новые возможности для крипторынков в РФ, Европе и ОАЭ
– почему криптовалюта становится все более привлекательной для бизнеса;
– законодательство о криптовалютах в ОАЭ;
– легальный сервис обмена для юридических лиц;
– возможности работы с криптовалютой.

Дмитрий Романов
Юрист-консультант блокчейн-проектов.
Правовое регулирование Метавселенной (виртуального пространства)
– концепция Метавселенной и проблемы ее правового регулирования;
– правой статус цифрового имущества в виртуальном пространстве и хозяйственных сделок, совершаемых с ним;
– пути реализации юридической ответственности в Метавселенной.

Василий Кулеш
Chief Communications Officer, Whitebird.io.
Легальное обращение криптовалют, налогообложение. Практические аспекты применения и перспективы развития
– особенности легального обращения и налогообложения криптовалют для физических и для юридических лиц: инвестирование, переводы, хранение, дарение и др.;
– практические аспекты применения, а также риски, возникающие при некорректном взаимодействии с криптовалютами и криптопроектами;
– перспективы развития криптоэкономики в 2023-2024 годах: CBDC, WEB 3 и др.

Татьяна Чепкова
Руководитель российского подразделения BeInCrypto — международного издания о криптовалютах, блокчейне и Web3-технологиях.
Медиа в эпоху Web3
– история медиа;
– почему старые модели не работают;
– как Web3-технологии влияют на эволюцию медиа;
– какие проблемы медиа можно решить при помощи Web3;
– Web2 vs Web3;
– пути развития.
Дмитрий Богданов
Основатель ведущей компании в мире по космической логистике и доставке малых спутников на орбиту Земли.
Практическое применение блокчейн- и Web3-технологий на примере создания системы проектного менеджмента в аэрокосмической отрасли
Блокчейн-технологии действительно позволяют создавать распределенные приложения, код которых выполняется на машинах участников сети. Это позволяет создавать распределенные системы управления проектами, которые позволяют участникам проекта обмениваться информацией и координировать свои действия на совершенном ином уровне прозрачности, достоверности и безопасности. Это делает систему и данные в ней крайне устойчивыми к техническим сбоям и вредоносным атакам. Вышеперечисленные критерии действительно позволяют находить применение блокчейн-технологиям в наукоемких и высокотехнологичных отраслях бизнеса, в частности, в аэрокосмической отрасли.

Дмитрий Алексейченко
CEO, криптоплатформа FREE2EX.
Инструменты заработка на централизованных криптобиржах: возможности и риски
– на чем могут зарабатывать криптотрейдеры, арбитражники и обычные люди;
– криптоактивы как способ диверсификации рисков;
– доход на токенизированных акциях, золоте и сырье;
– как потерять все деньги в 2023 году.

Александр Дульский
Руководитель отдела клиентского сервиса криптоплатформы BYNEX.
Метавселенная и ее связь с реальным миром
– почему о ней все говорят;
– может ли метавселенная заменить реальный мир;
– перспективы ее развития;
– можно ли зарабатывать в метавселенной.

Валерий Усенко
Team Lead Academy currency.
Криптотрейдинг в Беларуси: опыт, выводы, прогнозы
⁃ какие возможности и ограничения существуют для криптотрейдинга в Республике Беларусь;
⁃ успешный опыт контроля рисками;
⁃ ожидаемые тенденции на рынке криптовалют;
⁃ какие перспективы ждут трейдеров в будущем.
Ярослав Кабаков
Экономист, кандидат экономических наук. Директор по стратегии ИК “Финам”.
Криптовалюты и фондовый рынок: как криптовалюты взаимодействуют с традиционными рынками Криптовалюты, такие как биткойн, привлекают все больше внимания в финансовом мире, но как они связаны с традиционным фондовым рынком? Обсудим, как биткойн и другие криптовалюты взаимодействуют с фондовым рынком, и как инвесторы могут использовать криптовалюты в своих портфелях. Мы также рассмотрим перспективы биткойна и его роль в мировой экономике. Наконец, мы проанализируем, как традиционные инвестиции, такие как акции, облигации и индексы, сравниваются с инвестициями в криптовалюты.
Smart Contract. Product Management
Smart Contract. Product Management
08.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Product Management
Code
Smart Contract. Lending
Smart Contract. Lending
07.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Lending
Code
Smart Contract. Payment Channel
Smart Contract. Payment Channel
06.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Payment Channel
Code

Smart Contract. Remote Purchase
Smart Contract. Remote Purchase
05.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Remote Purchase
Code
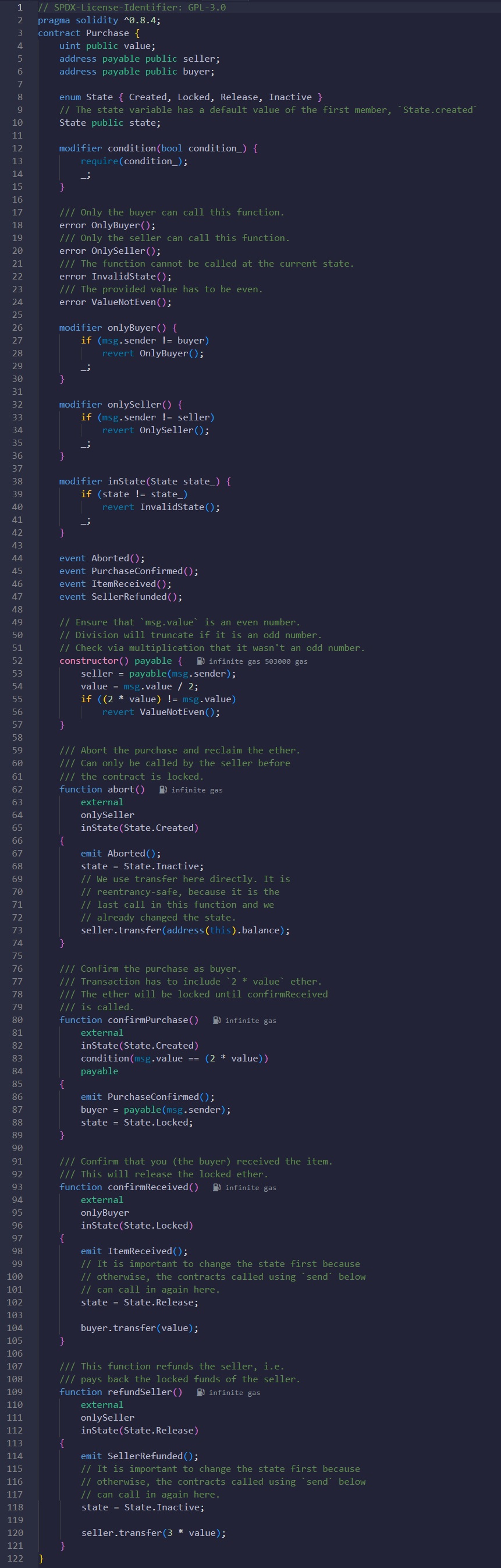
Smart Contract. English Auction for Tender Procedure
Smart Contract. English Auction for Tender Procedure
04.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for English Auction for Tender Procedure
Code

Smart Contract. Order Status Tracking
Smart Contract. Order Status Tracking
03.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Order Status Tracking
Code
Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
 Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
Smart Contract. Correspondent Account
02.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract for Correspondent Account
Code
Smart Contract. Public Offer Agreement
Smart Contract. Public Offer Agreement
01.01.2023
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Remix IDE, Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart Contract for Public Offer Agreement
Code
Personal exhibition “World Paper Money World“

Personal exhibition “World Paper Money World“
2022
1000+ Banknotes
People, animals, flowers, buildings and more
+bonus+
One Money Club
The full exhibition is here.
Personal exhibition “City Trip(p)er. 10 years of the Real World as it is”
 Personal exhibition “City Trip(p)er. 10 years of the Real World as it is”
Personal exhibition “City Trip(p)er. 10 years of the Real World as it is”
2022
1 World, 10 Seasons, 100+ Trips, 70 Countries, 300 Cities, 50 Events, 50 Places, 1000+ Photos, just Episode I
This personal exhibition contains the most interesting photos of city infrastructure solutions, weird and funny moments of life and people relationship.
Smile and evolve yourself. It’s all about it.
The full exhibition is here.
Intro
I have always believed that you need to live your life consciously.
If you can do this, at the end of your life it will not hurt you that you didn’t have time to do something.
And everyone must find their own answer to the question of how to do it.
My logical sequence is
- determine what areas your life consists of
- analyze each area
- set goals in each area to achieve them in the future
- spend your resources on achieving these goals
In case of changing life views, you can re-conduct this analysis.
And for me one of my top goals is traveling.
Planning
When planning my travels, I chose the way to visit a specific region and explore all the planned places and events.
My way to find such places and events is by analyzing the following lists
- Wonders of the World
- Natural Wonders of the World
- UNESCO World Heritage
- Sights of the region
- Map of the region
- Megacities in the region
- World events in the region
Realization
The rules for a successful travel are
- check visa requirements
- book accommodation and transfers
- buy insurance
- prepare copies of all documents on your smartphone and the Internet
- prepare cash and bank cards
- prepare photo equipment
- check the type of electrical outlets in the region
- have travel apps on your smartphone
- clean up the Feng Shui area in the house, which is responsible for traveling 😉
Top 30 photos

30. Industrial scale production

29. The main national support

28. The journey of a lifetime begins with the first step

27. Waiting for the rocket launch. Beautiful sunset today is not the main event

26. Personal freedom

25. State sea

24. Covid reality

23. Reality of censorship

22. Covid panorama view

21. On the Top

20. The capitalist approach is: to be the most inventive in your profession – seems to be the most successful

19. Pedestrian

18. Instead of washing glasses

17. Gorgeous

16. DiscipLine. German version

15. Simple Phila

14. Anything for the content. American version

13. Simple SanFran
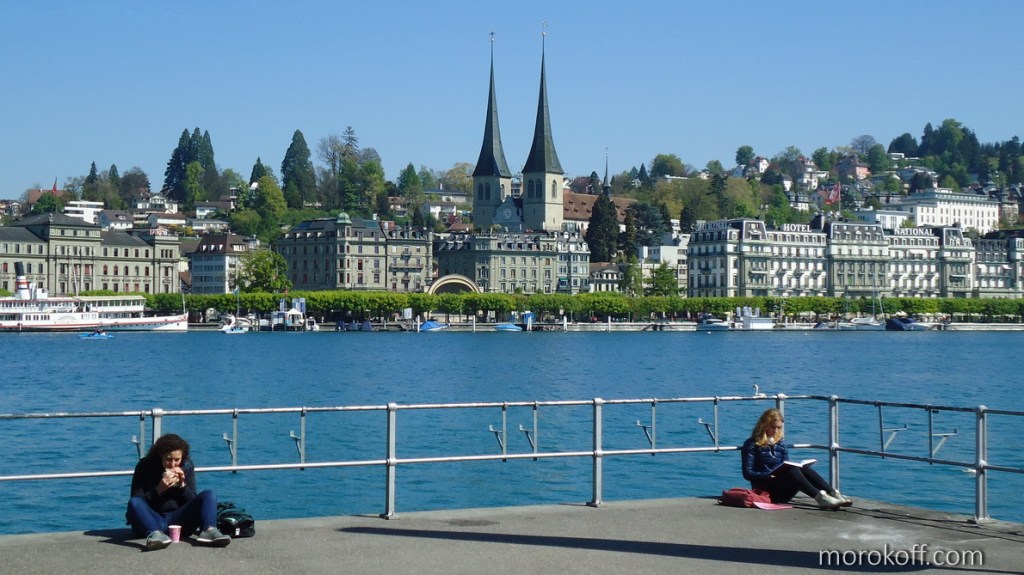

12. Free people

11. Cause and effect. Serbian version

10. Daily work

9. Will we have enough of ours?

8. Blessed fishing

7. Simple Vienna

6. Simple Newark

5. British family

4. The question and the answer

3. Simple Kiev

2. American naughtiness

1. Love is the brightest human feeling that guides you and gives you the purpose of your life
Season 10. Point S

Season 10. Point S
2022
Interesting and rare moments of everyday life of people in the South.
Season 1. Bonus.
City Insight
Belarus: Borisov, Kamianiuki, Kamyanyets, Zhodino
Kazakhstan: Baikonur, Korday, Kyzylorda, Nur-sultan
Russia: Dmitrov, Istra, Ivolginsk, Kaluga, Korolev, Kubinka, Monino, Ryazan, Sholokhovo, Tula, Tver, Ulan-Ude, Volokolamsk, Zvyozdny gorodok
Event Insight
Auto: BMW Fest 2022, Green Cars Day 2022, Motorsport Expo 2022, Oldtimer Rally 2022
Military: V-Day Parade 2022
Space: Soyuz MS-22
Sport: Baku 2022 Formula 1 Azerbaijan Grand Prix, Moscow 2022 Russian Drag Racing Championship, Stayki 2022 Belarus Drift Championship
Place Insight
Heritage: Gobustan
Space: Baikonur Cosmodrome
Wildlife: Yanardag
Season 3. Bonus.
City Insight
United Arab Emirates: Ajman
Event Insight
Sport: Abu Dhabi 2022 Formula 1 United Arab Emirates Grand Prix, Qatar 2022 FIFA World Cup
Place Insight
Resorts: Mercure Gold Hotel Dubai
Season 4. Bonus.
City Insight
Maldives: Hulhule, Hulhumale, Male
Sri Lanka: Ambalangoda, Anuradhapura, Colombo, Dambulla, Ella, Gampola, Kandy, Nuwara Eliya, Sigiriya
Event Insight
Politics: Aragalaya 2022
Place Insight
Heritage: Sigiriya fortress
National Parks: Yala
Plants: Damro Tea
Resorts: Hard Rock Hotel Maldives, Sheraton Maldives Full Moon Resort & Spa
Season 7. Bonus.
City Insight
Tanzania: Arusha, Dar es Salaam, Karatu, Moshi, Zanzibar
Place Insight
National Parks: Kilimanjaro, Ngorongoro, Tarangire
Season 8. Bonus.
City Insight
Indonesia: Bedoegoel, Denpasar, Jakarta, Labuan Bajo, Surabaya, Yogyakarta
Place Insight
National Parks: Komodo
Resorts: Hilton Bali Resort, Hyatt Regency Yogyakarta, Plataran Komodo Beach Resort
Stats: Countries 5 (70), Cities 48 (300), Events 12 (50), Places 16 (50)

Udemy.com Platform

Udemy.com
via Udemy.com Platform
04.06.2022
Online Educational Course “ECBA prep Training”
Online Educational Course “CBAP Prep Training”
Online Educational Course “CBDA prep Training”
Online Educational Course “CCBA Prep training”
Course content:
- Introduction
- BA planning and Monitoring
- Elicitation and Collaboration
- Req. LCM
- Strategy Analysis
- Requirement Analysis and Design Def
- Intro to Solution Evaluation
Udemy.com Platform
Udemy.com
via Udemy.com Platform
03.06.2022
Online Educational Course “What Is Business Analysis for Information Technology”
The content of the modules:
- Business Analysis – An Overview
- Strategic, Tactical, and Operational Business Analysis
- Requirements Defined
- Business Requirements
- Stakeholder Requirements
- Solution Requirements
- Transition Requirements
- An Introduction to Business Analysis Techniques
- What Tools Are Used?
- What Techniques Are Used?
- An Overview of Business Analysis and SDM/SDLC
- Business Analysis in Waterfall SDM
- BA Role in Iterative SDM
- Agile Projects and Business Analysis
- Business Analysis and the Future
Международная конференция “It Entrance 2022”

Международная конференция “It Entrance 2022”
28.05.2022
Отель Виктория «Олимп», Минск, Республика Беларусь + online
Международная конференция о способах войти воit.
Выступления:
 Игорь Мамоненко
Игорь Мамоненко
Генеральный директор Belhard
Вступительное слово
– Обзор рынка
– Газета KV
– Рынок труда
– Проекты Belhard

Александра Якимахо
Рroject Мanager в ООО “Оксаджайл”, тренер курса “Управление проектами в сфере разработки ПО” в “Академии Belhard”, психолог
Психология в проектном управлении
Выступление о том, какие есть роли и обязанности в сфере IT на стыке управления и психологии, какие инструменты коучинга и психологии вы можете применять для поддержки себя, самоорганизации и самомотивации в поиске работы и смене деятельности.
Презентация:








Даниил Поляков
Старший разработчик Android, Тинькофф
Мобильная разработка. Как начать?
Выступление о направлениях мобильной разработки, о курсах, которые помогут быстрее погрузиться в разработку, а также разберем шаги, которые нужно предпринять, чтобы стать крутым мобильным разработчиком.
Презентация:















Олег Кирасов
Преподаватель Института технологий информатизации и управления БГУ, Delivery Manager
ИТ образование в Беларуси: куда пойти учиться новичку?
Выступление о том, какая образовательная программа подойдет мне лучше всего? А будет ли эта профессия актуальна завтра? И почему фундаментальное образование играет в этом всем важную роль, но подойдёт оно не всем?
Презентация:







Эдвард Хомицкий
СЕО IT Digital Progress. Прошел путь от Junior-специалиста до CEO IT компании.
Правильная постановка целей и их достижение в сфере IT
Выступление о целях и приоритетах. Как планировать свое время. Как выстраивать приоритеты. Конкретные примеры реальных людей. Как правильно фокусироваться на задачах и их выполнять. Продуктивность в IT. Как не бросить IT на пол пути. Как получить результат.

Яна Осадчая
Специалист по маркетингу, rabota.by
Аналитика рынка труда, фишки создания резюме в 2022 году
Выступление о сервисе rabota.by, статистике и анализе рынка труда, создании резюме и общении с HR-специалистами и заказчиками.

Зинаида Пчелинцева
Специализируется на продажах в Западной Европе, США, Канаде, Австралии и Азии. Имеет обширный опыт работы с основными техниками продаж и каналами лидогенерации: нетворкинг, социальные сети, ревью-платформы, профессиональные сообщества, email-рассылки.
Как войти в профессию IТ Sales Manager
Выступление на тему, кто такие Sales Managers и что они едят, как понять, подходите ли вы для этой позиции, как получить заветную позицию в крутой компании.
Презентация:



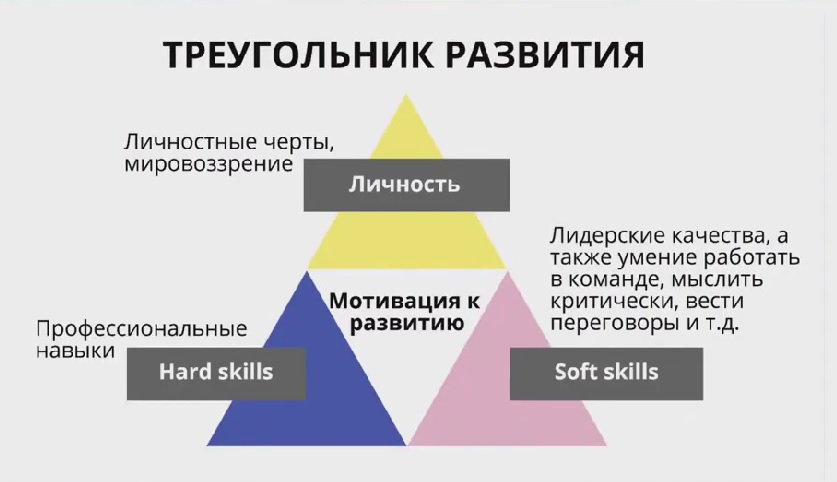






Алексей Заговалко
Начальник лаборатории испытаний средств защиты в ОДО “Вирусблокада”, тренер курса “Защита информации и информационная безопасность” в “Академии Belhard”
Работа в сфере информационной безопасности: возможности и перспективы
Выступление о том, что представляют из себя современные специалисты, работающие в сфере информационной безопасности? Какими навыками и знаниями они обладают? С какими задачами им приходится сталкиваться? Какие смежные профессии близки к сфере информационной безопасности? С этими и многими другими вопросами мы и попытаемся разобраться в рамках данного доклада.
Coursera: University of Pennsylvania
 University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania
via coursera.org Platform
31.01.2022
Online Educational Course “English for Career Development“
Syllabus:
Season 9. Point N
Season 9. Point N
2021
Interesting and rare moments of everyday life of people in the North.
Season 1. Bonus.
City Insight
Belarus: Logoysk, Naroch, Silichy
Russia: Alexandrov, Bogolyubovo, Irkutsk, Ivanovo, Kazan, Khuzhir, Kindasovo, Kolomna, Kostroma, Listvyanka, Lyaskelya, Olonets, Pereslavl-Zalessky, Petrozavodsk, Rostov, Sortavala, Staraya Sloboda, Slyudyanka, Suzdal, Sviyazhsk, Veliky Novgorod, Vladimir, Volgograd, Yaroslavl, Yoshkar-Ola, Zhukovskiy
Event Insight
Aero: MAKS 2021
Sport: Euro 2020
Place Insight
Wildlife: Baikal, Ruskeala, Shkhery
Season 2. Bonus.
City Insight
Albania: Berat, Durres, Fier, Fushe-Kruje, Golem, Kruja, Lushnje, Pojan, Tirana
Macedonia: Ohrid
Place Insight
Heritage: Apollonia
Season 3. Bonus.
City Insight
Egypt: Dahab, Nuweibaa, Sharm El-Sheikh
Turkey: Alanya, Konaklı, Manavgat, Side
United Arab Emirates: Dibba Al Fujairah
Place Insight
Wildlife: Cappadocia
Stats: Countries 2 (65), Cities 47 (252), Events 2 (38), Places 7 (34)
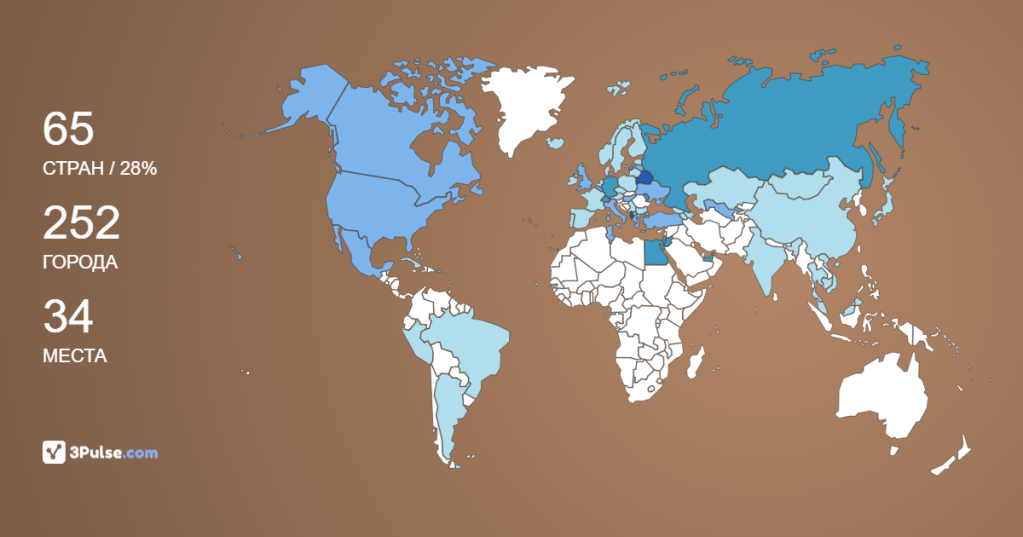
Национальный центр правовой информации Республики Беларусь
Национальный центр правовой информации Республики Беларусь
30.06.2021
Минск, Беларусь
Семинар “Особенности организации и проведения закупок товаров (работ, услуг) за счет собственных средств в 2021 году”
Тематика
Информационно-поисковая система “Эталон-online”
Нормативная база
Практические кейсы
Коррупционные риски
Фото
Свидетельство
Журнал “Тендер”
№ 40 (1005)
26.10.2020
Статья “Смарт-тендер – наше будущее?″ (продолжение)
В статье представлен механизм проведения тендера с использованием технологии блокчейн.
Журнал “Тендер”
Журнал “Тендер”
№ 39 (1004)
19.10.2020
Статья “Смарт-тендер – наше будущее?″
В статье представлен механизм проведения тендера с использованием технологии блокчейн.
Solidity Project: Tender Voting
Project: Tender Voting
18.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: The application allows members of the tender committee to vote for the winner when evaluating participants. Such voting is open and immutable.
Results
Solidity Project: Improvement Stage
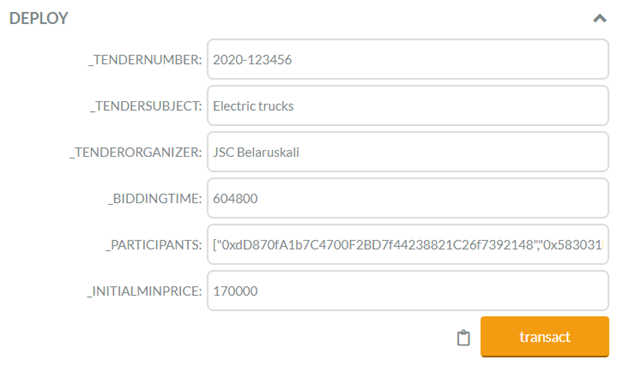
Project: Improvement Stage
17.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract allows you to initiate Improvement Stage of the tender on the Blockchain network and submit improved commercial proposals.
Smart Contract

Screens
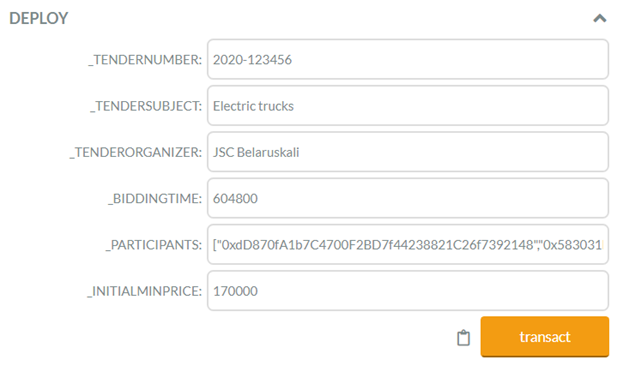



Solidity Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
 Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
Project: Submitting Initial Commercial Offers
16.10.2020
Blockchain ecosystem: Ethereum
Programming Language: Solidity
Technologies: Ganache, Truffle, Metamask, Git
Github: here
Description: Smart contract allows you to initiate a tender on the Blockchain network and submit initial commercial proposals.
Smart Contract

Screens